Figure 2.
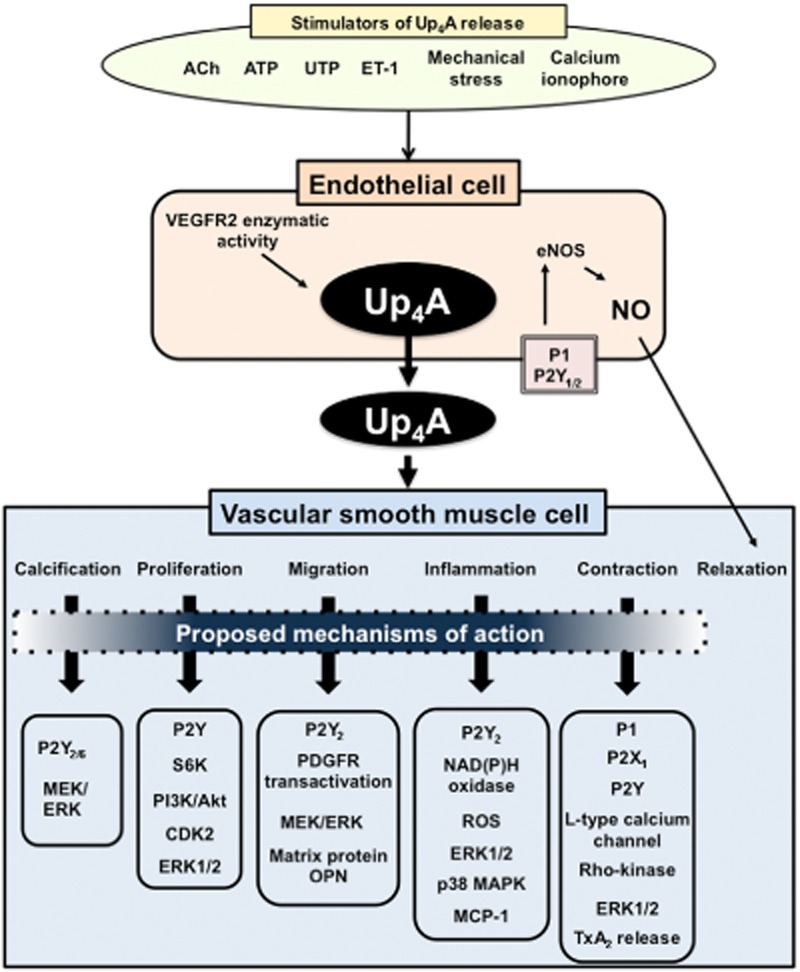
Effects of Up4A on vascular smooth muscle functions. When EC are stimulated with, for example, ACh, ATP, uridine triphosphate (UTP), ET-1, mechanical stress or Ca2+ ionophore (A23187), Up4A is generated. Released Up4A acts in both ECs and vascular SMC. In ECs, Up4A binds to P2Y1/2 or P1 receptor and activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS); releasing NO and producing relaxation. In vascular SMCs, Up4A leads to calcification, proliferation, migration, inflammation and contraction. Details are shown in text.
