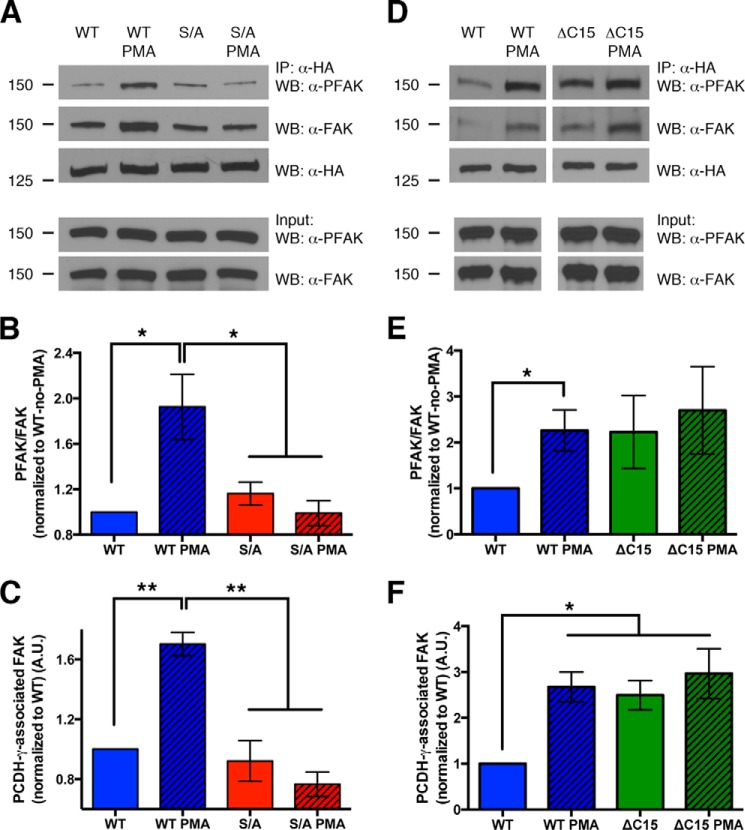
FIGURE 5.
Phosphorylation of Ser-922 disrupts γ-Pcdh inhibition of, but not binding to, FAK. A, lysates of HEK293 cells co-transfected with HA-tagged γ-Pcdh A3-WT or A3-S/A and GFP-FAK immunoprecipitated with anti-HA to pull down γ-Pcdh-associated FAK. PMA treatment did not disrupt the ability of A3-WT to bind FAK but did result in a higher proportion of A3-associated FAK being phosphorylated (PFAK). PMA treatment has no effect on activation state of A3-S/A-associated FAK, confirming the role of PKC phosphorylation of Ser-922. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot. B and C, quantification of three experiments performed as in A. The ratio of PFAK to total FAK associated with A3 was calculated and normalized to the no-PMA A3-WT ratio (B). Total amount of FAK pulled down with A3-WT, but not A3-S/A, actually increased after PMA treatment (C). D–F, experiments were similar to those shown in A–C but compared A3-WT to A3-ΔC15. Loss of the C-terminal lipid binding domain led to more FAK being pulled down, similar to the effect of PMA treatment on A3-WT, although as expected ΔC15 is insensitive to PMA as it lacks Ser-922 (D and F). The ratio of PFAK/FAK in ΔC15 co-immunoprecipitations trended higher, but due to high variability in these experiments this difference was not statistically significant (D and E). Graphs show the means ± S.E. of three (A–C) or 6 (D–F) experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.