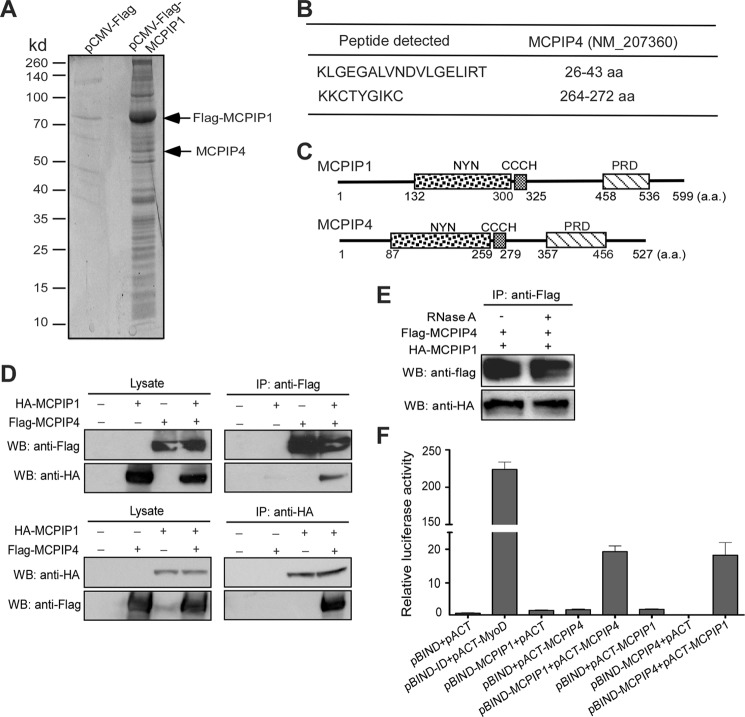
FIGURE 1.
Identification of MCPIP4 as a MCPIP1-interacting protein. A, HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-MCPIP1 or pCMV-Flag vector. After 24 h, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by anti-Flag M2-agarose beads. After wash, the immunoprecipitates were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and stained by Spyro Ruby; B, stained bands were excised out and analyzed by LTQ-orbitrap-velos mass-spectrometer. Two fragments targeted on MCPIP4 amino acid sequence were indicated. C, scheme of MCPIP1 and MCPIP4 protein domains. D, HA-tagged MCPIP1 and Flag-tagged MCPIP4 expression vectors were co-transfected into HEK293 cells. Cell lysates were prepared and incubated with either anti-HA or anti-Flag beads to precipitate MCPIP1 and MCPIP4, respectively. The cell lysates and immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-HA or anti-Flag antibodies. E, HA-tagged MCPIP1 and Flag-tagged MCPIP4 expression vectors were co-transfected into HEK293 cells. Cell lysates were incubated with anti-Flag beads to precipitate MCPIP4. The immunoprecipitates were treated with RNase A (100 unit/ml) for 30 min and then subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-HA or anti-Flag antibodies. F, mammalian two-hybrid assay for the interaction of MCPIP1 and MCPIP4. Different combinations of pBIND- and pACT-derived expression vectors were co-transfected with a reporter containing five Gal4 binding sites upstream of a minimum promoter-drive luciferase gene into HEK293 cells. The luciferase activity was measured using a dual-luciferase assay system. Data are presented as mean ± S.D., n = 4.