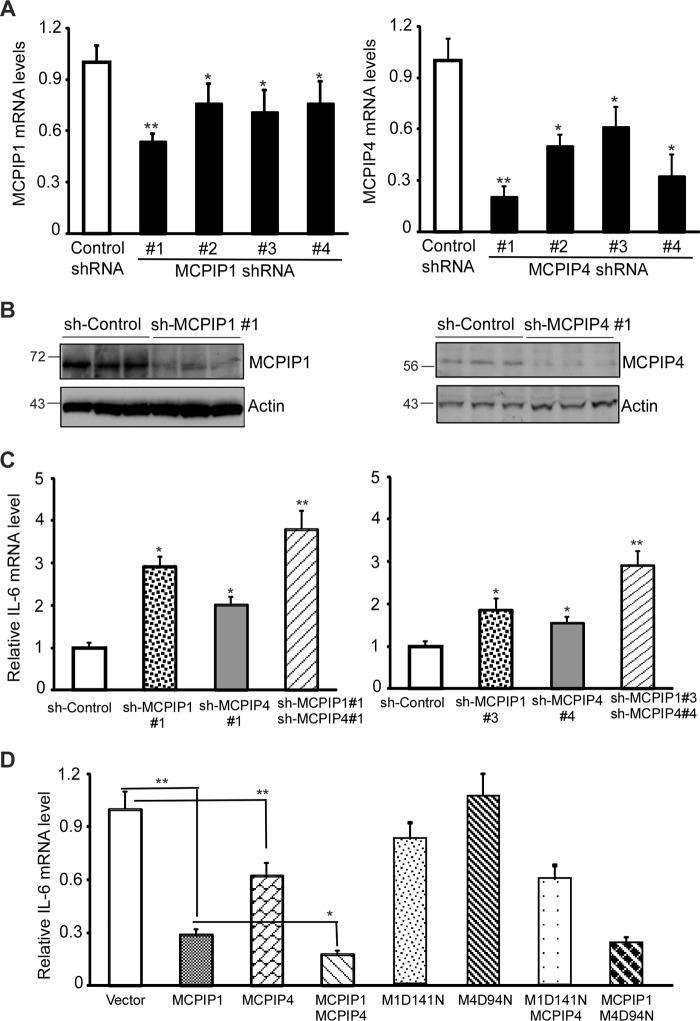
FIGURE 6.
MCPIP1 and MCPIP4 additively contribute to control the IL-6 mRNA levels in activated macrophages. A, plasmids encoding four sets of shRNA targeting different positions of mouse MCPIP1 mRNA or MCPIP4 mRNA and control shRNA were transfected into RAW264.7 cells, a murine macrophage cell line. After 48 h of transfection, the transfected cells were treated with 20 ng/ml of Pam3CSK4 for 6 h. The mRNA levels of MCPIP1 and MCPIP4 were examined by QPCR. Data are presented as mean ± S.D., n = 4, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus control group. B, MCPIP1 and MCPIP4 protein levels in shRNA-transfected RAW264.7 cells were detected by Western blot with anti-MCPIP1 (Genetex) or anti-MCPIP4 (Proteintech). Actin was served as loading control. C, RAW264.7 cells were transfected with the plasmids encoding two-sets of different shRNAs as indicated and then treated with Pam3CSK4 (20 ng/ml) for 6 h. The mRNA level of IL-6 was examined by QPCR. Data are presented as mean ± S.D., n = 4, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus sh-control group. D, RAW264.7 cells were transfected with the expression vector for MCPIP1, MCPIP4, MCPIP1(D141N) (M1D141N), MCPIP4(D94N) (M4D94N), or their combinations as indicated. After 24 h, the transfected cells were treated with Pam3CSK4 (20 ng/ml) for 6 h. The mRNA level of IL-6 was examined by QPCR. Data are presented as mean ± S.D., n = 4, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.