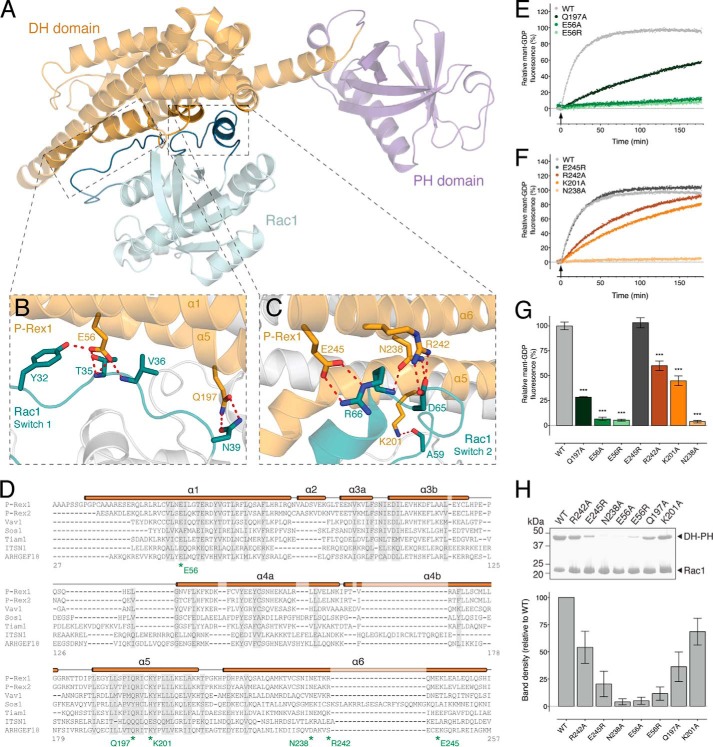
FIGURE 3.
Structural basis of Rac1 activation by P-Rex1. A, location of the Rac1 switch 1 and switch 2 interaction interfaces within the P-Rex1·Rac1 structure. B, P-Rex1 DH domain residues Glu-56 and Gln-197 interact with the switch 1 region of Rac1. C, P-Rex1 DH domain residues Lys-201, Asn-238, Arg-242, and Glu-245 mediate interactions with the switch 2 region of Rac1. D, multiple sequence alignment of P-Rex1 family members with related GEFs. The P-Rex1 secondary structure is illustrated above the alignment with residues targeted for mutational analysis indicated. E, the rate of in vitro GEF activity of the P-Rex1 DH-PH domain was significantly decreased for E56R, E56A, and Q197A mutants. F, the rate of in vitro GEF activity of the P-Rex1 DH-PH domain was significantly decreased for R242A, K201A, and N238A, but not E245R, mutants. Curves show the average of at least three independent experiments. G, GEF activity at 60 min following P-Rex1 DH-PH addition. H, impaired interactions between wild-type His6-Rac1 and untagged P-Rex1-(1–404) mutants compared with the wild-type control. Error bars indicate means ± S.E. ***, p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparison test. The activity of the mutants is expressed relative to the wild-type P-Rex1 DH-PH domain. Binding was assessed by pulldown assays using His6-Rac1 bound to Ni-NTA-agarose beads. Purified untagged wild-type P-Rex1 and the indicated P-Rex1 mutants were added to the pulldown assay at a concentration of 1 μm.