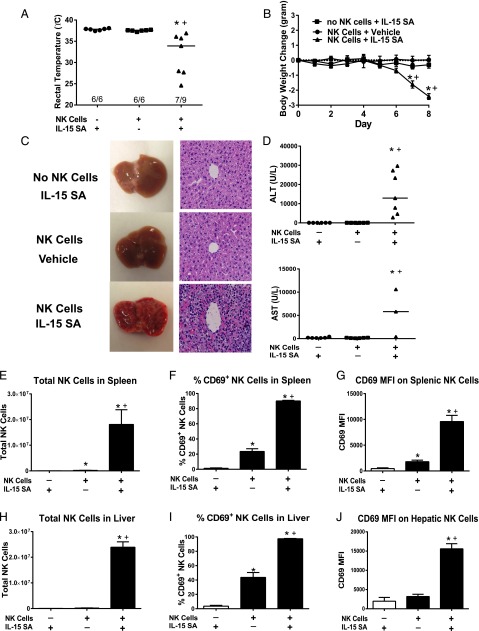
FIGURE 6.
Toxicity of IL-15 SA in Rag2−/−γc−/− mice receiving adoptive transfer of WT NK cells. WT NK cells (1.0 × 106 cells/mouse) were injected i.v. into Rag2−/−γc−/−mice 3 h before the initiation of IL-15 SA (2 μg) treatment. Rag2−/−γc−/− mice that received NK cell transfer and vehicle treatment or IL-15 SA treatment without NK cell transfer served as control. (A) Body temperature was measured at 8 d after NK cell transfer and IL-15 SA treatment. (B) Body weight was measured at the indicated time points. (C) Liver gross morphology and H&E-stained liver sections (original magnification ×400) at 8 d after treatment. Olympus BX43 microscope and Olympus digital color camera DP73 were used for acquisition of the H&E-stained images. (D) ALT and AST concentrations in serum at 8 d after adoptive transfer and IL-15 SA treatment. Splenocytes and hepatic leukocytes were harvested at 8 d after NK cell transfer and IL-15 SA treatment. The numbers of splenic and hepatic NK cells (E and H) and CD69 expression by NK cells (F, G, I, and J) was determined using flow cytometry. n = 6–9 mice/group. Data are representative of two separate experiments. *p < 0.05 compared with mice that did not receive NK cell transfer and were treated with IL-15 SA, +p < 0.05 compared with mice that received NK cell transfer but not IL-15 SA treatment.