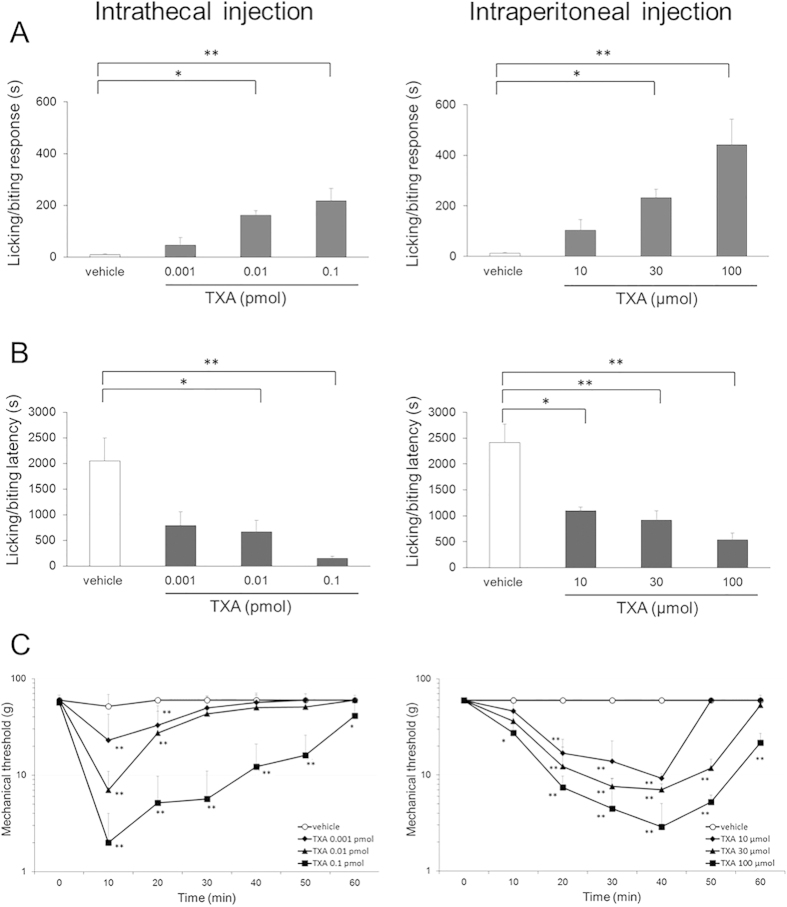
Figure 1. Assessment of behavioral response to intrathecal and intraperitoneal injection of tranexamic acid (TXA).
(A) Total time devoted to licking/biting responses during a 60-min observation period is increased in a concentration-dependent manner by intrathecal or intraperitoneal injection of TXA. (B) The latency to the start of the behavior is shortened in a concentration-dependent manner by intrathecal or intraperitoneal injection of TXA. (C) Mechanical thresholds for paw withdrawal in response to von Frey stimulation are significantly reduced in a concentration-dependent manner by intrathecal or intraperitoneal injection of TXA. Concentrations of intrathecal or intraperitoneal injected TXA range from 0.001 to 0.1 pmol and from 10 to 100 μmol, respectively. The data are given as mean ± SD. In each dose group, n = 5; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by one or two-way ANOVA.