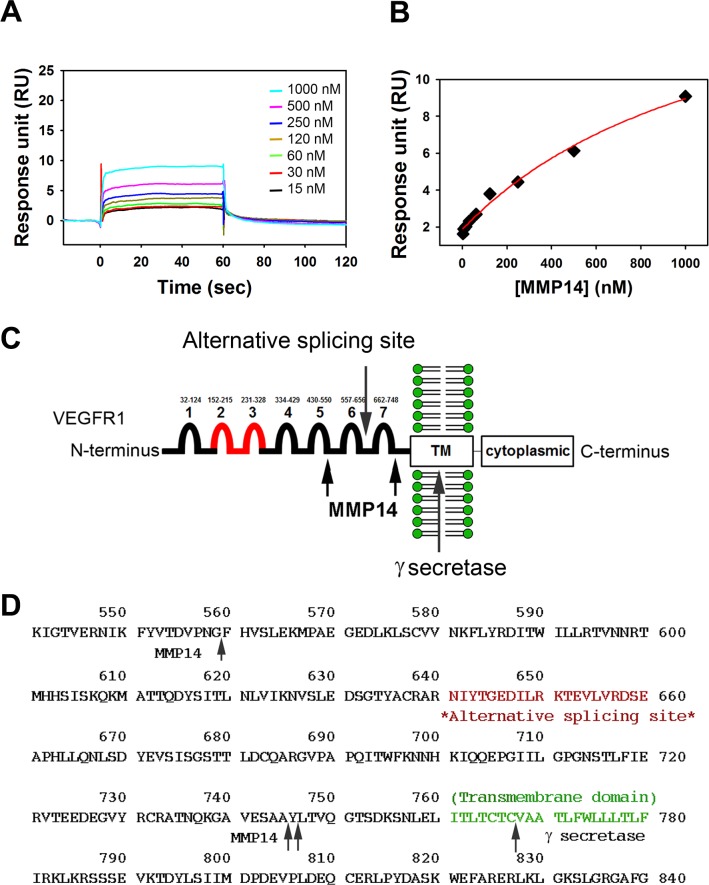
Figure 2.
MMP14 binds rmVEGFR1 and cleaves putative VEGFR1 at two points in the extracellular domain. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analyses determined the equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) between MMP14 and immobilized rmVEGFR1. Sensorgrams (A) and a fitting curve (B) are shown. (C) Diagram of the products of MMP14 cleavage of rmVEGFR1 based on Edman sequencing results (in parentheses). An N-terminal fragment (SKLKVP) corresponding to aa27 to 560 (Ig domains 1–5) forms a 59.8-kDa monomer that does not dimerize. A middle fragment (FHVSL[E]K) corresponding to aa560 to 744 (Ig domains 6–7) forms a 21-kDa monomer that does not dimerize. A C-terminal fragment (YLTVQGTSDK) corresponding to aa745-C-terminus corresponds to a 70-kDa dimer/35-kDa monomer that contains the recombinant human IgG1/His domains. Proposed sites of VEGFR1 processing by MMP14 are shown relative to known sites of γ-secretase processing and the point at which homology ends between full-length and soluble VEGFR1 proteins (alternative splicing site). (D) MMP14 cleavage sites in the VEGFR1 protein sequence.