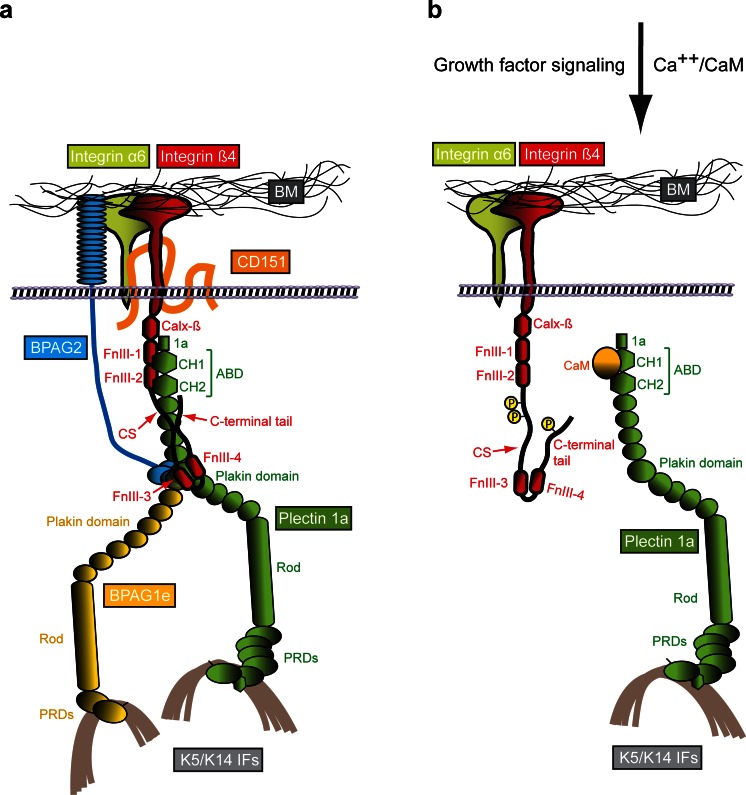
Fig. 2.
Molecular organization of HDs and a model of the HD disassembly mechanism. a Schematically drawn are the six key components of type I HDs (integrin subunits α6 and β4, CD151, BPAG2, BPAG1e and plectin 1a), the extracellular basement membrane (BM) containing the ligand laminin-332 and the intracellular binding partner, intermediate filaments (IFs) of the keratin (K5/K14) type. The various protein domains involved in binding of integrin β4 to plectin 1a and in the linkage of the HD complex to keratin IFs are indicated. b Mechanism of growth factor-induced dissociation of the integrin β4–plectin 1a complex. For simplicity, only integrin α6β4, plectin 1a and K5/K14 IFs are shown. Growth factor-induced phosphorylation of serine residues in the C-terminal integrin β4 tail and CS domains results in the dissociation of integrin β4 from plectin 1a’s plakin and ABD domains. Subsequent interaction of plectin 1a’s ABD with the Ca++-bound form of calmodulin (CaM) prevents re-association of the integrin β4-plectin 1a complex. 1a, isoform-specific N-terminal domain preceding the ABD of plectin 1a; Calx-β, Na+–Ca2+ exchanger motif; CH1,2, calponin homology domains 1 and 2; CS, connecting segment; FnIII-1,-2,-3,-4, fibronectin type III domains 1–4; PRDs, plectin repeat domains