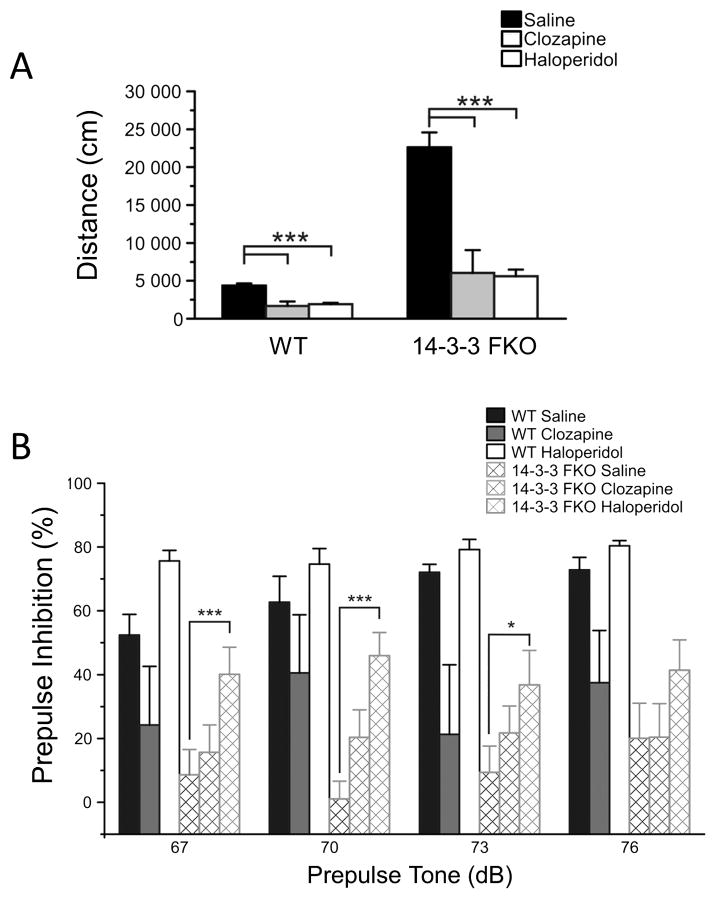
Figure 3. The effects of antipsychotic drugs on schizophrenia-related behavior deficits of the 14-3-3 FKO mice.
(A) Administration of clozapine (WT, N = 7; 14-3-3 FKO, N = 8) or haloperidol (WT, N = 6; 14-3-3 FKO, N = 8) attenuates the hyperactivity of the 14-3-3 FKO mice in open field testing. (B) Prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response was measured in WT and 14-3-3 FKO mice after administration of saline (WT, n = 7; 14-3-3 FKO, n = 9), clozapine (WT, n = 7; 14-3-3 FKO, n = 13) or haloperidol (WT, n = 6; 14-3-3 FKO, n = 12). In the 14-3-3 FKO mice, haloperidol increased PPI at 67, 70 and 73 dB prepulse tones to similar PPI percentages of saline injected WT mice. Clozapine did not alter PPI at any prepulse tone levels in the 14-3-3 FKO mice compared with saline injected 14-3-3 FKO mice. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M., with statistical significance denoted by: *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, comparisons between genotypes and drug administration groups were performed using two-way ANOVA.