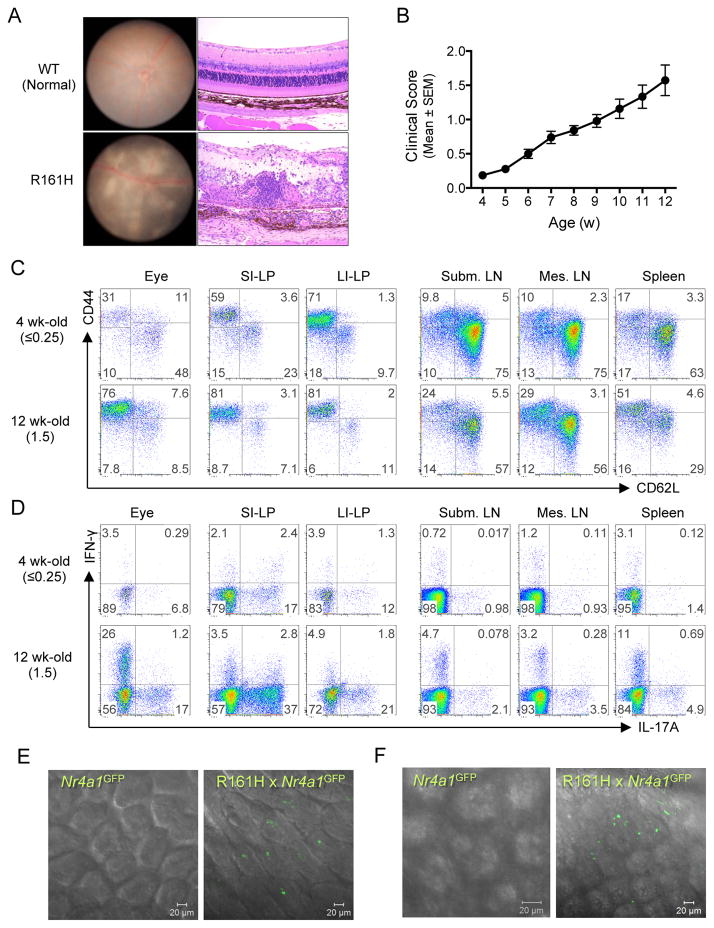
Figure 1. R161H mice develop spontaneous uveitis that is associated with presence of activated T cells in the gut.
(A) Spontaneous uveitis in R161H mice. Fundus photography (left) and histology (right) of healthy WT and uveitic R161H retina.
(B) Kinetics of disease development in R161H mice. Clinical scores were determined weekly by fundus examination.
(C and D) R161H CD4+ T cells in the intestine show an effector/memory phenotype. Representative CD4+ T cell plots for activation/memory markers (C) and Th17 phenotype (D) in various tissues from 4 wk-old (clinical score ≤0.25) and 12-wk old (clinical score 1.5). Intracellular IL-17A and IFN- γ were detected following 4 h ex vivo stimulation with PMA and ionomycin in the presence of Brefeldin A.
(E and F) Expression of Nr4a1 (encoding Nur77) was detected by GFP (green) in fresh ileum samples of Nr4a1GFP reporter mice at 17 days of age (E, before disease onset) and adult (F, after onset). Single plane of the Z stack is shown. Also see Figure S1, Movies 1–4.