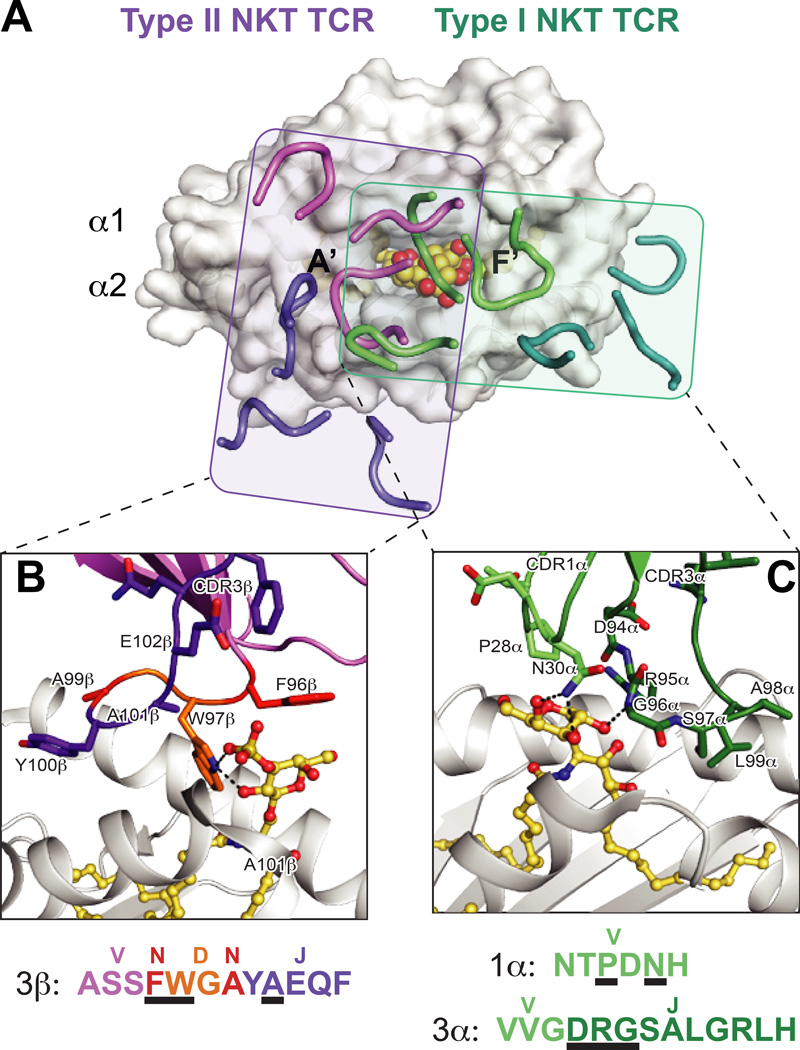
Fig. 3. Differential docking modes and lipid antigen contacts of Type I and Type II NKT TCRs.
(A) Footprints of the Type I (iNKT) and Type II NKT TCRs on CD1d. The complex structures of the murine iNKT and Type II NKT TCR structures are aligned by CD1d. Shown is the surface of murine CD1d-αGalCer (PDB ID: 3HE7) with the CDR loops of the murine Vβ7 iNKT TCR (PDB ID: 3HE7) in green (α chain) and teal (β chain), and type II NKT TCR (PDB ID: 4EI5) in purple (α chain) and pink (β chain). The rough borders of the TCR/CD1d interfaces are shown as shaded boxes colored teal (Type I) and purple (Type II). (B) Detail of the mouse Type II NKT TCR-CD1d–sulfatide interface. Residues that contact the sulfatide antigen are shown and colored according to origin of encoding nucleotides (pink = V, purple = J, orange = D, red = non-templated). CD1d is shown in grey cartoon, sulfatide is in yellow ball-and-sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown in black dashed lines. Lower panel details the amino acids of the CDR3β loop, colored according to origin as above, with black underlines denoting with residues contact sulfatide. The major sulfatide contacts are through either non-templated or D-encoded TCR residues. (C) Detail of the mouse Vβ7 iNKT TCR –CD1d-αGalCer interface. Residues that contact the αGalCer antigen are shown and colored according to origin of encoding nucleotides (light green = V, dark green = J). . CD1d is shown in grey cartoon, αGalCer is in yellow ball-and-sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown in black dashed lines. Lower panel details the amino acids of the CDR1α and CDR3α loops, colored according to origin as above, with black underlines denoting with residues contact αGalCer. All contacts with the lipid antigen and germline encoded.