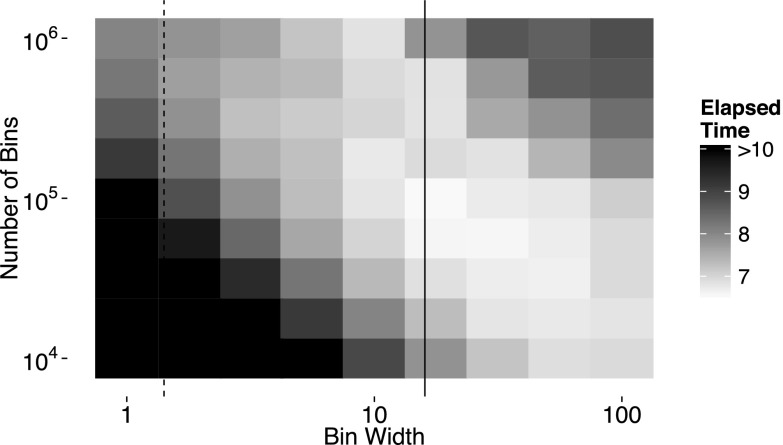
FIG. 3.
Simulation time for various bin widths and number of bins. In this example, M = 107 and every propensity = 10−7 (the propensity sum equals one). The dashed line corresponds to the theoretical optimal bin width that minimizes the total search depth. The solid line corresponds to W = 16, which is the target bin width used in practice. The algorithm performs well over a fairly wide range of bin widths and number of bins. As the problem size increases, the optimal number of bins increases roughly proportional to .