Figure 7.
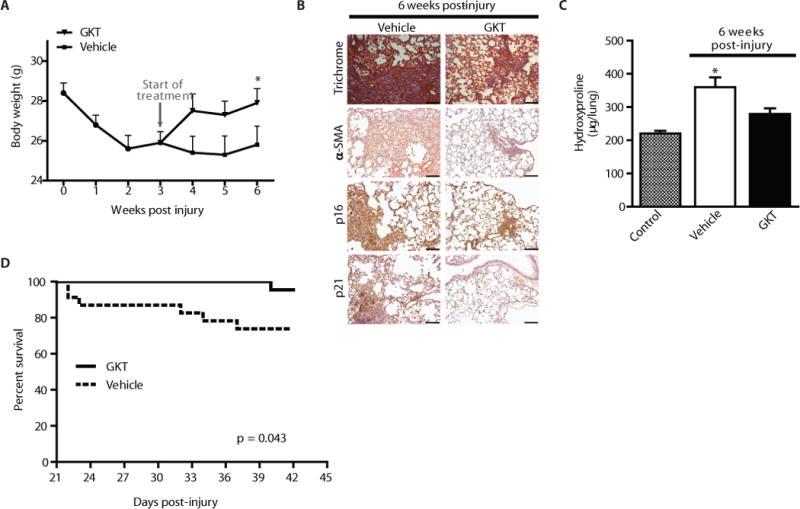
In vivo pharmacologic targeting of Nox4 with GKT137831 leads to reversal of age-associated persistent fibrosis. (A–D) Aged mice (18 m) were subjected to bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Starting at 3 weeks post-injury, mice were treated daily with GKT137831 (40 mg/kg) or vehicle by oral gavage through week 6 (21 treatments total). Body weight of the mice was recorded weekly (A); values represent mean ± s.e.m.; n = 17–21 per group; *p value < 0.05, compared to vehicle-treated controls. (B–C) Lung tissues were harvested from control (uninjured) or at 6 weeks post-injury. Tissues were evaluated by Masson’s trichrome blue staining for collagen and by immunohistochemical analyses was performed to evaluate expression of α-SMA and senescence markers (p16 and p21) (B). Whole lung homogenates were analyzed by quantitative hydroxyproline assay (C); data are expressed as total μg of hydroxyproline/whole lung; values represent mean ± s.e.m.; n = 9–10 per group; *p value < 0.05, compared to all other groups. Kaplan-Meier survival curve for GKT137831 (n = 22) and vehicle (n = 23) treated mice (D); log-rank test, p < 0.05. Scale bars, 100 μm.
