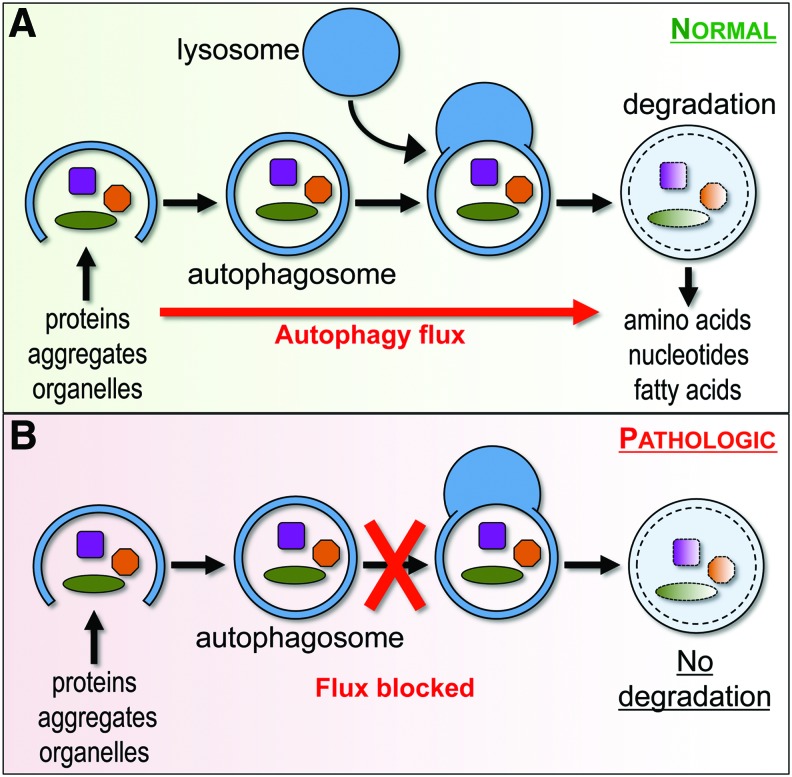
FIG. 2.
Autophagy flux under normal and pathological conditions. (A) During autophagy, double-membrane vesicles (autophagosomes) sequester cytoplasmic components, including damaged organelles and toxic protein aggregates, and then fuse with lysosomes to allow degradation of cargo by lysosomal proteases. This progress of cargo through the autophagy system is termed autophagy flux and generally serves a cytoprotective function. (B) Under pathological conditions, autophagy flux may be blocked, for example due to lysosomal defects. This can lead to accumulation of dysfunctional autophagosomes and contribute to cell damage and death. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars