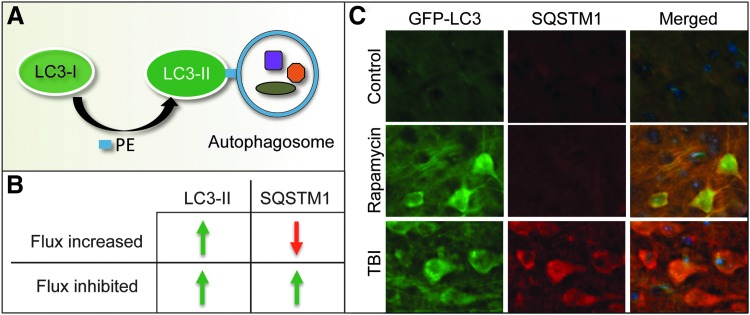
FIG. 3.
Common methods used to assess autophagy and autophagy flux. (A) When autophagy is induced, cytosolic LC3-I protein is covalently conjugated to PE to form LC3-II, which translocates to the autophagosomal membrane. Accumulation of LC3-II can be measured as a marker of autophagosome formation. (B, C) Comparison of LC3-II and SQSTM1 levels under conditions when autophagy flux is increased or inhibited. (B) When flux is induced, numbers of autophagosomes and levels of LC3-II increase but levels of autophagy substrates such as SQSTM1 decrease. When autophagy flux is blocked, both numbers of autophagosomes (LC3-II) and autophagy substrates (SQSTM1) increase. (C) Comparison of levels of LC3 (GFP-LC3 fluorescence—green) and SQSTM1 (immunohistochemistry—red) in the cortex of GFP-Lc3 transgenic autophagy reporter mice under conditions when autophagy flux is induced (in vivo Rapamycin treatment for 48 h) versus when autophagy flux is inhibited (24 h after controlled cortical impact injury). Data adapted from Sarkar et al. (53) with permission of authors. PE, phosphatidylethanolamine.