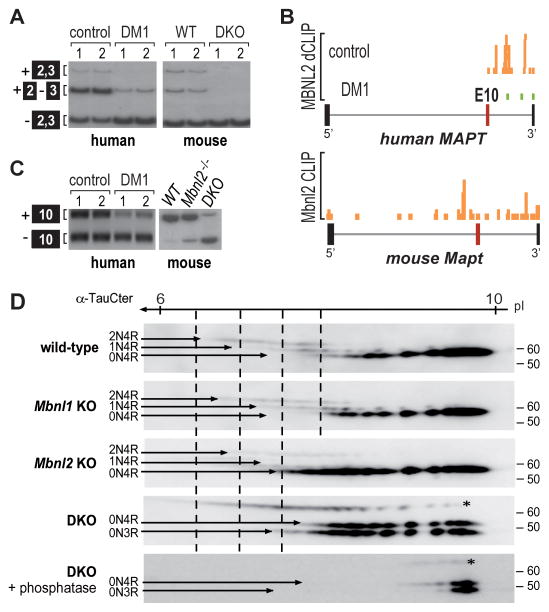
Figure 5. Tau Isoform Mis-regulation in DM1 and Mbnl DKO Brain.
(A) RT-PCR splicing analysis showing shift toward skipping of MAPT exons 2 and 3 in DM1 brain compared to controls and in Nestin-Cre DKO brain relative to WT.
(B) MBNL2 binding is reduced near MAPT exon 10 in DM1 brain compared to controls. UCSC browser view of MBNL2 dCLIP binding profiles near MAPT exon 10 (alternative exon, red box; flanking exons, thick black boxes; introns, gray lines) in control (orange) and DM1 (green) brain (n = 3). Bottom panel shows the mouse Mbnl2 HITS-CLIP binding profile near exon 10.
(C) RT-PCR analysis of MAPT/Mapt exon 10 splicing for human control versus DM1 and mouse wild-type (WT), Mbnl2 KO (Mbnl2−/−) and Nestin-Cre DKO (DKO).
(D) Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (1st dimension, 3 to 11 non-linear pH gradient strips; 2nd dimension SDS-PAGE) and immunoblot of tau isoforms (2N4R, 1N4R, 0N4R and 0N3R) in WT, Mbnl1ΔE3/ΔE3 (Mbnl1 KO), Mbnl2 ΔE2/ΔE2 (Mbnl2 KO) and Nestin-Cre DKO brain. Bottom panel corresponds to tau staining after treatment with lambda phosphatase. Tau protein was stained with the α-TauCter antibody. The N-terminal inserts correspond to inclusion/exclusion of alternative exon 2 and exon 2 + 3. The 3R and 4R isoforms correspond to isoforms without/with the exon 10 encoding sequence.