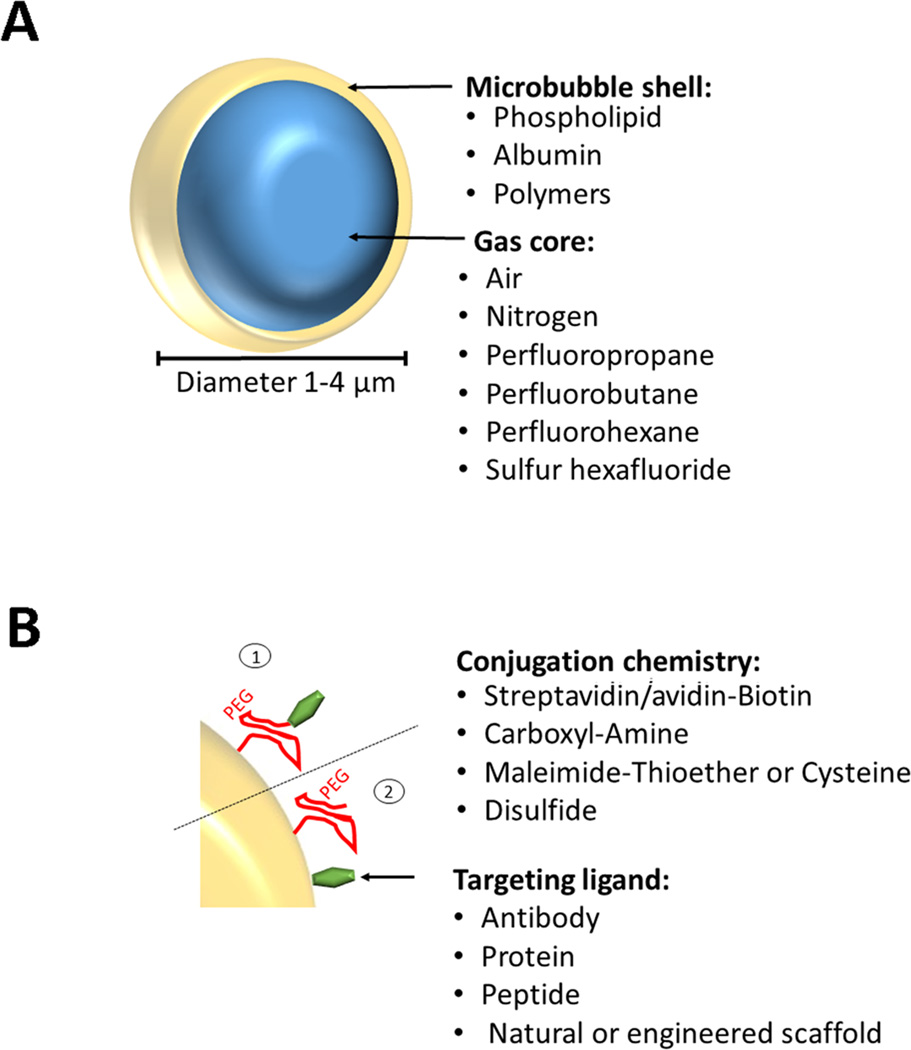
Figure 1. Design of molecularly-targeted microbubbles.
(A) Microbbubles are 1–4 µm microspheres with a shell composed of various materials and a core that can contain different types of gases. (B) Incorporated PEG chains stabilize the microbubble shell, form a steric barrier to prevent coalescence, minimize adsorption of macromolecules to the microbubble surface, and provide spacing between the shell and binding ligands. Various types of ligands (e.g., antibodies, proteins, peptides) can be attached non-covalently or covalently by using biotin/streptavidin, biotin/avidin, amine (NH2)/amide, maleimide/thioether, 2-(Pridylthio)propionyl (PDP)/disulfide, either via the PEG arm (1) or directly onto the shell surface (2).