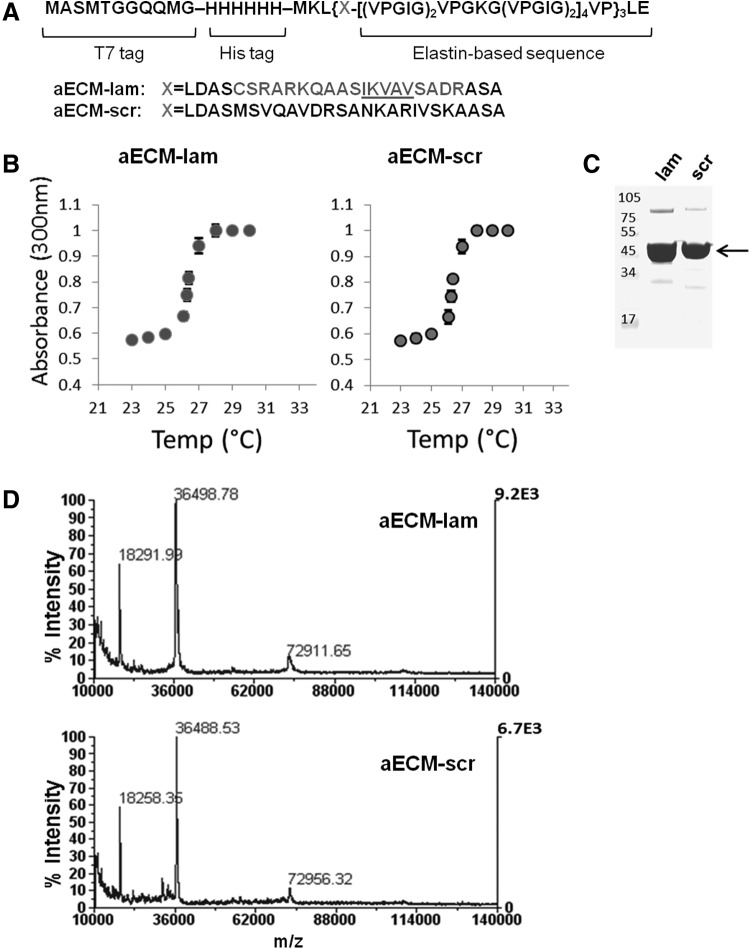
FIG. 1.
Purification and characterization of aECM proteins. (A) aECM proteins were cloned into pET28a and expressed under the control of a T7 promoter in BL21 (DE3) E. coli. The laminin-elastin and scrambled-elastin hybrid sequences are shown. (B) Turbidity of aECM solutions as a function of temperature was measured at 300 nm to determine the LCST of aECM-lam and aECM-scr. (C) Purified aECM proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained by Colloidal blue. Arrow indicates that the major bands migrated with the expected mobility of the aECM proteins. Note also the presence of dimer at around 72 kDa. (D) Both samples were analyzed with MALDI-TOF, showing major peaks at ∼36.5 kDa, 18.3 kDa, and 73 kDa. The peak at 18.2 kDa is likely due to double-charging of the protein; that at 72.9 kDa is due to dimerization. aECM, artificial extracellular matrix; LCST, lower critical solution temperature.