Figure 2. The role of the Dll4-Notch axis in cardiovascular and metabolic disorders.
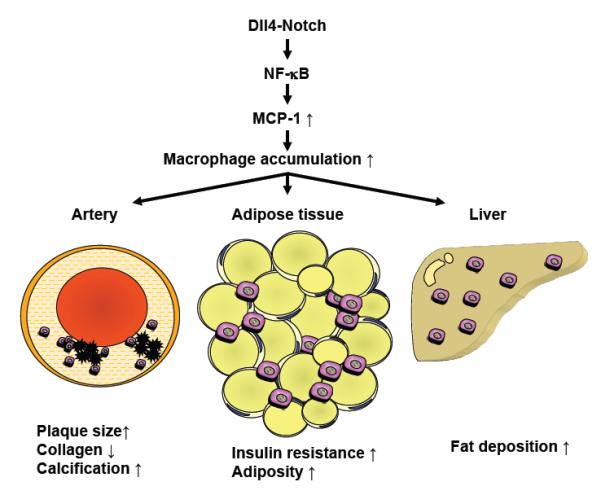
The Dll4-mediated Notch signaling activates the NF-κB pathway. Activation of NF-κB increases the expression of MCP-1, which leads to the accumulation and pro-inflammatory activation of macrophages in organs such as arteries, adipose tissue, and the liver. Accumulation of activated macrophages contributes to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, including atherosclerosis, insulin resistance, and fatty liver disease. (Partly modified with permission from Fukuda D, et al8.)
