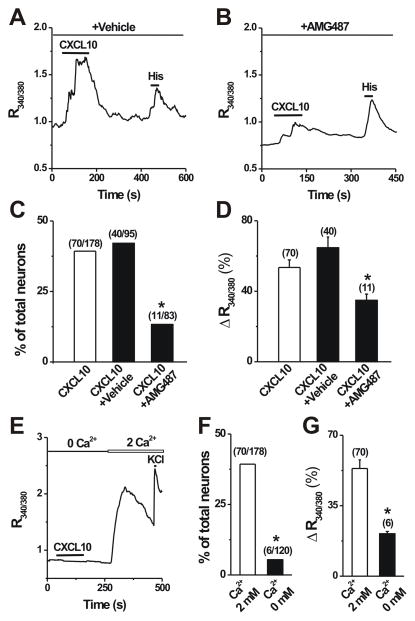
Figure 3.
The dependence of CXCL10-induced Ca2+ responses on functional CXCR3 receptors and the presence of extracellular Ca2+. A–B, Representative Ca2+ response to CXCL10 (50 nM, 2 min) in the presence of a specific CXCR3 antagonist AMG487 (10 μM in 0.1% DMSO vehicle) vs. in the presence of the vehicle alone. C–D, Pretreatment with AMG487 for 3 min but not vehicle significantly reduced the percentage of CXCL10-responsive neurons (Fisher’s exact test) and the mean magnitude of CXCL10-evoked Ca2+ response (unpaired t test). *p < 0.05 versus vehicle. E, Representative Ca2+ response in a neuron to CXCL10 in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ (0 mM) and KCl (50 mM) in presence of 2 mM extracellular Ca2+, respectively. F–G, Removal of extracelluar Ca2+ almost abolished CXCL10-evoked Ca2+ rise. Numbers of neurons tested are in parentheses.*p < 0.05 versus 2 mM Ca2+; Fisher’s exact test (F) or unpaired t test (G).