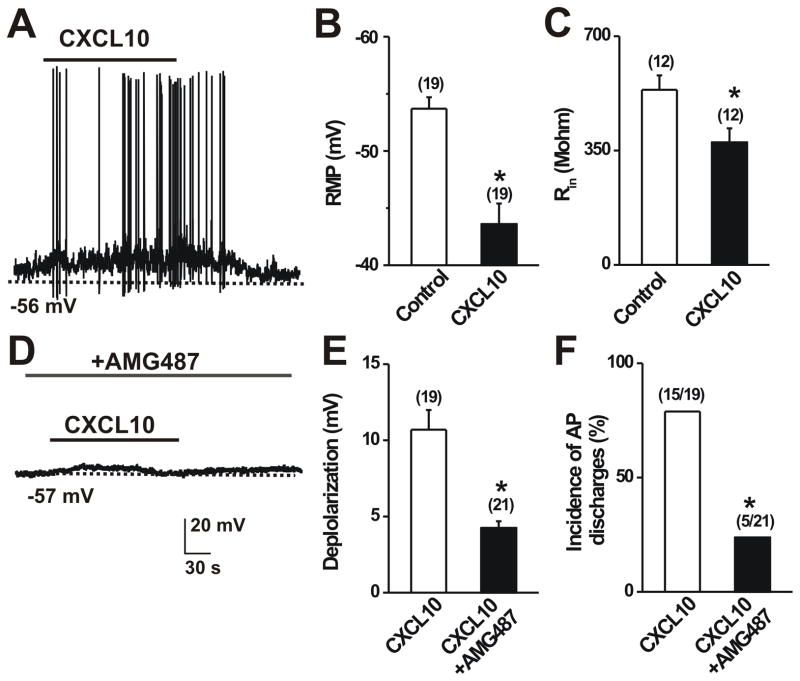
Figure 4.
CXCL10 increased neuronal membrane excitability after CHS. In each panel, neurons were tested that exhibited DiI labeling transported from SADBE challenged skin. A, Typical current clamp recordings of CXCL10-induced membrane potential depolarization and action potential discharges. Black bars above the traces indicates the duration of CXCL10 (50 nM; 2 min) application. B–C, Mean resting membrane potential (RMP) and mean input resistance (Rin) before (control) and during application of CXCL10. CXCL10 significantly depolarized the RMP and reduced the Rin. *p < 0.05 versus control, paired t tests. D, Representative current clamp recordings of CXCL10 application in presence of AMG487 (10 μM). E–F, Pretreatment with AMG487 significantly reduced the mean magnitude of CXCL10-induced membrane depolarization (paired t test) and decreased the incidence (percentage) of neurons exhibiting action potentials (Fisher’s Exact test). The number of cells responding and/or tested are in parentheses. *p < 0.05 versus control.