Fig. 3.
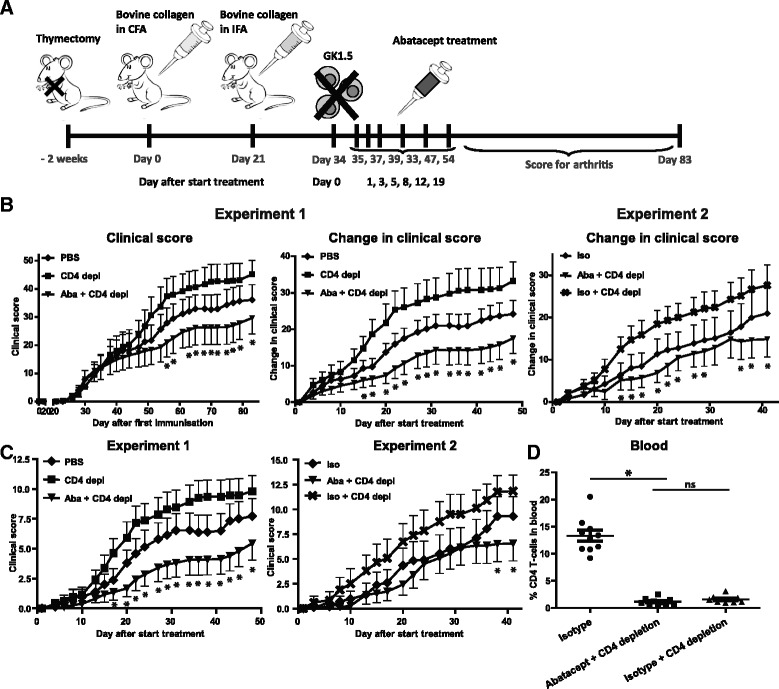
Abatacept decreased disease activity in thymectomized mice depleted of CD4+ T cells. a Collagen-induced arthritis was induced in male DBA/1 mice 2 weeks after they were thymectomized. When 80 % of the mice showed signs of arthritis, treatment was started. One day before the start of treatment, CD4+ T cells were depleted by intraperitoneal administration of GK1.5 and then the depletion was continued until the end of follow-up. Treatment was administered by intraperitoneal injection of PBS (diamonds), GK1.5 (squares; CD4 depl) or the combination of GK1.5 and abatacept (triangles; Aba + CD4 depl). The mice were scored three times per week for inflammation in the paws to monitor disease progression. b Clinical scores and changes in clinical scores starting from the day treatment was initiated in the different treatment groups (experiment 1; n=10 per treatment group). The same experiment was independently repeated in another 10 mice per treatment group, and an isotype for abatacept was used as control treatment (diamonds; iso) and in combination with CD4 depletion (cross symbols; iso + CD4 depl) (experiment 2). Changes in clinical scores starting from the day treatment was initiated are depicted. c The clinical scores of the paws that did not show signs of arthritis at the start of treatment are depicted for experiments 1 and 2. d The frequency of CD4+ T cells in blood at the end of follow-up was determined by flow cytometry. Abatacept-only treatment is not depicted to improve the readability of the graphs. Values are mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t test. *P < 0.05 abatacept + CD4 depletion vs control group. CFA complete Freund’s adjuvant, IFA incomplete Freund’s adjuvant, ns not significant, PBS phosphate-buffered saline
