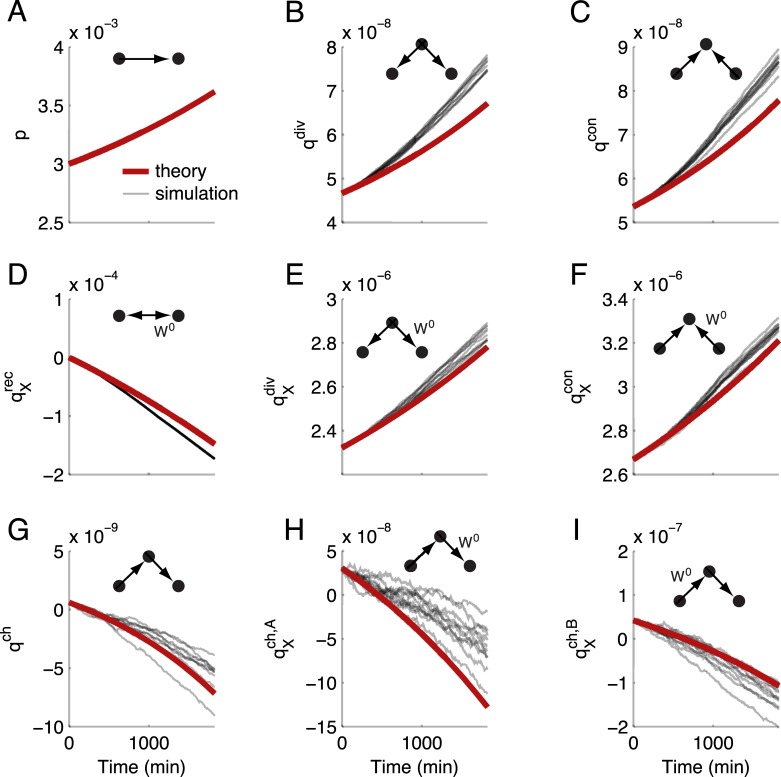
Fig 7. Reduced theory for the plasticity of two-synapse motifs.
In each panel, the strength of a different motif or mixed motif is plotted as it evolves. Red: theoretical prediction (Eqs (42)–(50)). Shaded lines: individual trials of the same initial network. (A) Mean synaptic weight. (B) Divergent motifs. (C) Convergent motifs. (D) Mixed recurrent motifs (strength of connections conditioned on their being part of a two-synapse loop). (E) Mixed divergent motifs (strength of individual synapses conditioned on their being part of a divergent motif). (F) Mixed convergent motifs. (G) Chain motifs. (H) Mixed chains type A (strength of individual synapses conditioned on their being the first in a chain). (I) Mixed chains type B (strength of individual synapses conditioned on their being the second in a chain). The STDP rule was in the depression-dominated balanced regime, as in Fig 6B.