Fig. 2.
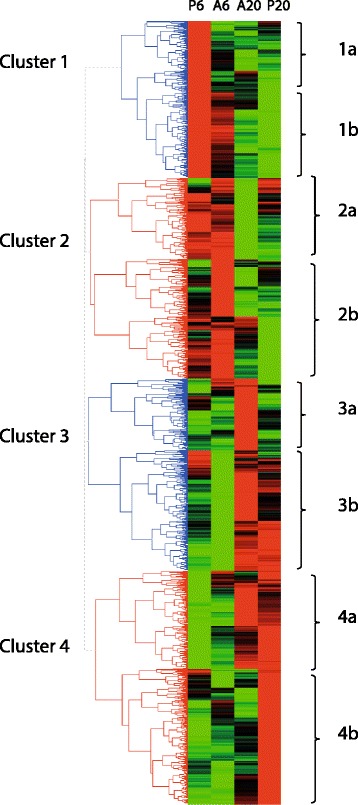
Clustering of differentially expressed pea genes in response to A. euteiches and P. pisi. Hierarchical clustering of all differentially expressed genes (P ≤ 0.05, ≥ 1.5 fold induction or ≤ 0.67 fold repression) at 6 hpi and 20 hpi compared to the mock-inoculated control samples generated by HCE3.5 software with the complete linkage method and the Manhattan distance measure. Red and green represent up regulated and down regulated genes, respectively. Four classes of genes were defined according to their expression profiles. Cluster 1 and 4 corresponds to genes highly up regulated at 6 hpi and 20 hpi in response to P. pisi (P6 and P20, respectively), while cluster 2 and 3 corresponds to genes up regulated at 6 hpi and 20 hpi in response to A. euteiches (A6 and A20, respectively). Each cluster was urther divided into smaller sub-clusters containing genes with common regulatory patterns. Sub-clusters 1b and 2a included genes induced in response to both pathogens at 6 hpi, while sub-clusters 1a and 2b included genes specifically induced in response to P. pisi and A. euteiches at 6 hpi, respectively. Sub-clusters 3b and 4a included genes induced in response to both pathogens at 20 hpi, while sub-clusters 3a and 4b represented genes specifically induced at 20 hpi in response to A. euteiches and P. pisi, respectively
