Fig. 2.
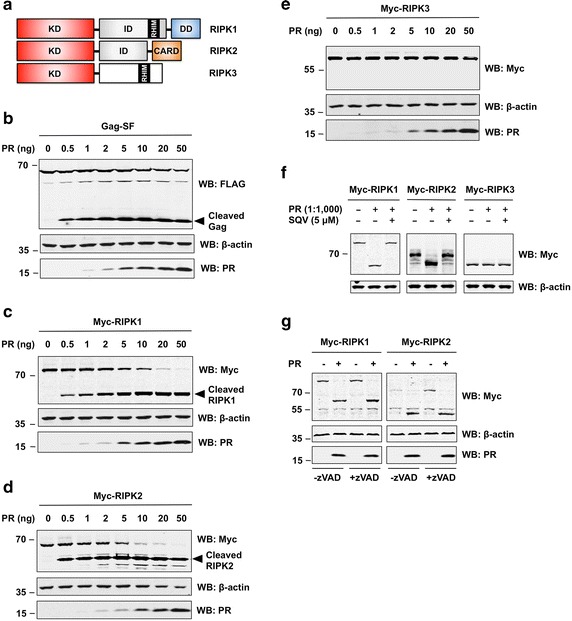
HIV-1 PR cleaves RIPK1 and RIPK2. a Domain architecture of RIPK family members. CARD caspase activation and recruitment domain, DD death domain, ID intermediate domain, KD kinase domain, RHIM RIP homotypic interaction motif. Illustration adopted from Festjens et al. [47]. b–e HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Gag-SF (b), or Myc-tagged RIPK1 (c), RIPK2 (d), and RIPK3 (e) along with increasing amounts of plasmid encoding HIV-1 PR. After 24 h, cells were collected in lysis buffer and samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and WB analysis. Proteins were revealed using antibodies against FLAG (for Gag), c-Myc (for RIPKs), β-actin, or HIV-1 PR. (F) HIV-1 PR cleaves RIPK1 and RIPK2 in vitro. HEK293T cells were transfected with expression plasmids encoding Myc-tagged RIPK1, RIPK2 or RIPK3. Cell lysates were prepared 24 h after transfection and incubated with recombinant HIV-1 PR (at a weight-to-weight ratio of 1000:1) in the absence or presence of SQV (5 μM). After 3 h of incubation at 37 °C, lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and WB. Proteins were revealed using antibodies against c-Myc or β-actin (loading control). g HIV-1 PR cleaves RIPK1 and RIPK2 in the absence of caspase activity. HEK293T cells were transfected with expression plasmids encoding Myc-tagged RIPK1 or RIPK2 with (+) or without (−) catalytically active HIV-1 PR in the absence or presence of pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk. Cells were lysed 24 h after transfection and total cell extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE and WB. Proteins were revealed using antibodies described above
