Fig. 2.
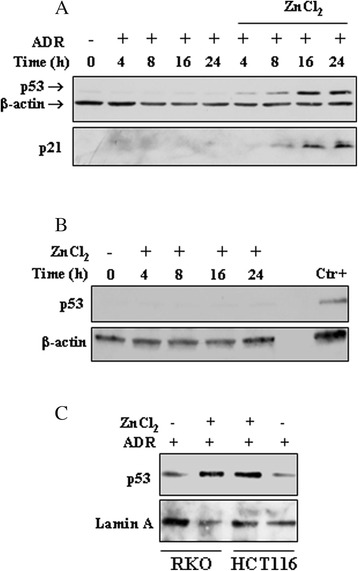
ZnCl2 induces p53 nuclear accumulation and activation in the presence of low-dose ADR. (a) HCT116 were treated with low-dose ADR (0.1 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of ZnCl2 (100 μM), for 4-8-16-24 h. Equal amounts of total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis for the detection of the expression levels of p53 and p21. Anti-β-actin was used as protein loading control. The samples derive from the same experiment and gels/blots were processed in parallel. One representative set of blot from three independent experiments, all generating similar results, is shown here. (b) RKO were treated with ZnCl2 (100 μM), for 4-8-16-24 h and the expression levels of p53 was detected by western blotting. A positive control for p53 expression in the same cells, is included (ADR 2 μg/ml for 16 h). Anti-β-actin was used as protein loading control. (c) RKO and HCT116 were treated with low-dose ADR (0.1 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of ZnCl2 (100 μM), 8 h. Equal amounts of nuclear extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE and p53 levels detected by western blotting. Anti-Lamin A was used as protein loading control. The gels have been run under the same experimental conditions and one representative set of blot from three independent experiments, all generating similar results, is shown here
