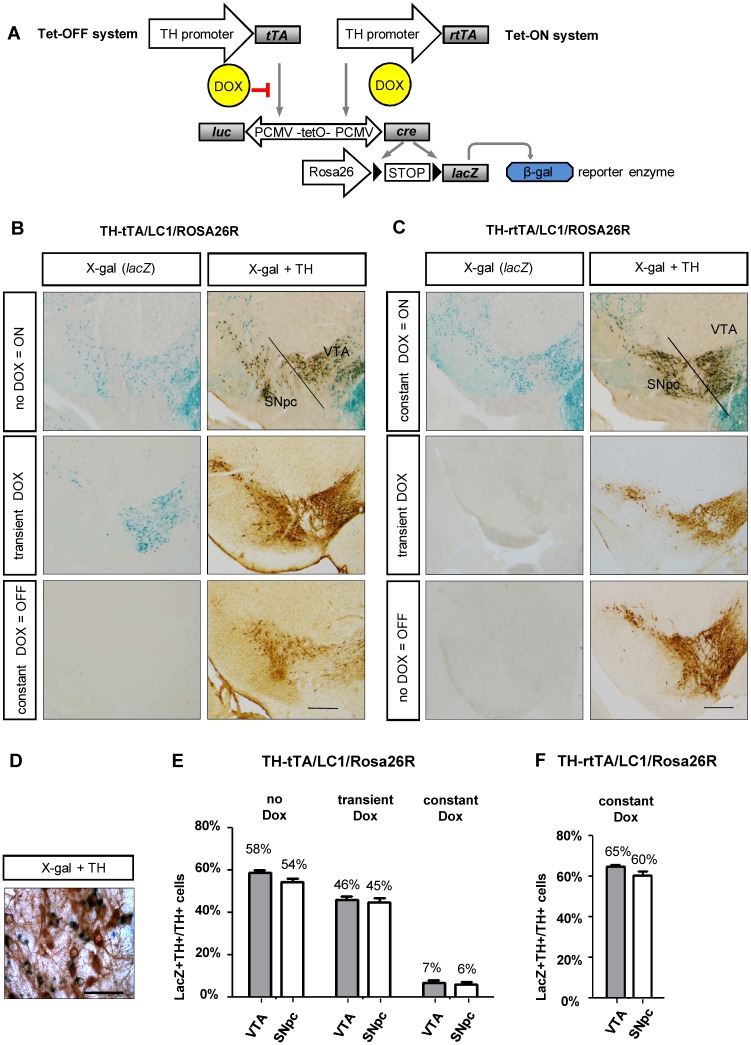
Fig 1. Specificity, inducibility and efficacy of gene expression in TH-tTA/LC1/Rosa26R and TH-rtTA/LC1/Rosa26R mice.
(A) Genetic scheme of DOX-regulated reporter gene expression in TH-tTA and TH-rtTA mice crossed with LC1 and Rosa26R reporter mice. (B and C) Coronal midbrain brain sections with substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) DA neurons of TH-tTA/LC1/Rosa26R (B) and TH-rtTA/LC1/Rosa26R (C) mice raised with or without doxycycline (DOX) or transiently with DOX to have the system switched off during development (TH-tTA mice treated with DOX during pre- and postnatal development till 6 weeks of age; TH-rtTA mice raised without DOX) and on during analysis (TH-tTA mice from the age of 6 weeks without DOX; TH-rtTA mice from the age of 6 weeks with DOX). Sections were stained for β-galactosidase activity with X-gal to visualize cells with activated tet-system. Adjacent sections were X-gal stained and co-stained with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) antibodies and DAB substrate (brown) to mark DA neurons. (D) Zoom in picture of TH and lacZ double positive cells in the SNpc. (E and F) Quantification of TH and lacZ double positive cells (LacZ+TH+) in the SNpc and VTA to estimate recombination efficacy in DA neurons (TH+) of animals treated constantly (constant DOX), transiently (transient DOX) or without DOX (no DOX) in the tet-OFF (E) and tet-ON mice (F). mean + s.e.m.; n = 3. Scale bars: 500 μm (B and C), 50 μm (D).