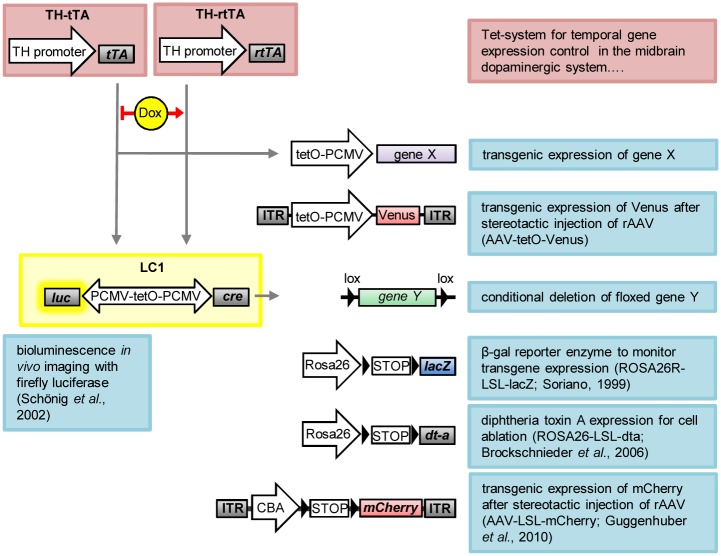
Fig 6. Schematic overview of utilized transgenic mice and recombinant AAV (rAAV) constructs.
TH-tTA and TH-rtTA mice express, under the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter, the tetracycline-regulated transactivator protein (tTA) or the reverse tetracycline-regulated transactivator protein (rtTA) in dopaminergic (DA) neurons. tTA binds to the tetracycline operon (tetO) in the absence of doxycycline (DOX) and rtTA binds in the presence of DOX, driving transient expression of gene X, for example the fluorescent protein Venus from a recombinant AAV vector (AAV-tetO-Venus), or luciferase and Cre from the LC1 construct. The LC1 encodes a luciferase enzyme, which can be used for bioluminescence in vivo imaging, and the Cre recombinase for deleting gene Y or removing floxed STOP codons (LSL). Cre is used here as a genetic switch to activate, from the ROSA locus, either expression of the reporter gene lacZ (encoding β-galactosidase) to visualize transgene expression or to activate expression of diphtheria toxin protein A (dt-a) to selectively induce cell death of DA neurons. Here we use Cre also to activate expression of the fluorescent protein mCherry from AAV-LSL-mCherry.