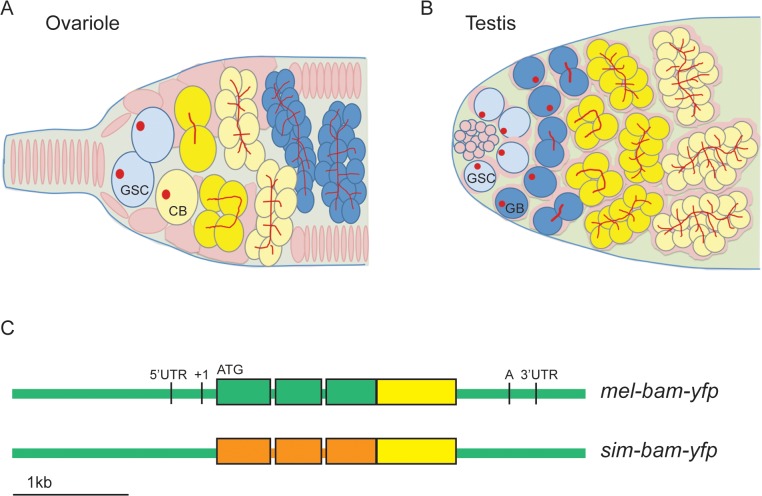
Fig 1. bam transgenic constructs.
(A) Diagrams of ovariole tip and (B) testis tip of wildtype flies. GSCs differentiate into cystoblasts (CB, ovariole) or gonialblasts (GB, testis), which undergo four synchronous, mitotic divisions. In females, Bam expression (yellow) is restricted to the CB, 2-,4-, and 8-cell cysts. In males, Bam expression occurs in 4-,8-, and 16-cell cysts. Somatic cells/somatic stem cells are shown in pink, germ cells in blue and yellow (when expressing Bam), GSCs in light blue, and spectrosomes (in GSCs) and fusomes (in cysts) in red. (C) bam transgenic constructs. All constructs are drawn to scale and contain the entire bam open reading frame (thick bars), 2 small introns, and non-coding regions (thin bars). Green color corresponds to D. melanogaster sequences, orange to D. simulans sequences, and yellow to the YFP coding sequence. ATG denotes the start codon, and 5’ and 3’ UTR sequence boundaries are from D. melanogaster genome release v. 5.30 (Flybase) [106]. The transcription start site is denoted as +1 [21] and the poly(A) addition sequence is denoted as A [23].