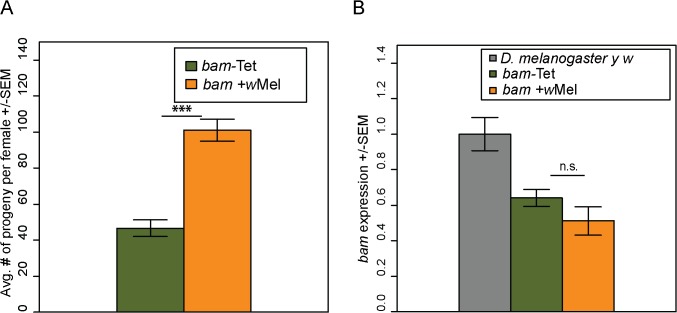
Fig 8. Wolbachia increases the fertility of D. melanogaster bam hypomorphs without altering bam RNA levels.
(A) One female and two tester males were allowed to mate and the trio was removed from the vial after 8 days. Fertility is shown as the average number of progeny per female +/- SEM for each vial. N = 20. Wolbachia-infected (wMel) bam hypomorphs are significantly more fertile than uninfected bam hypomorphs, bam-Tet (t-test, ***P<0.001). (B) qRT-PCR of ovarian mRNA from D. melanogaster bam hypomorphs with and without Wolbachia. The D. melanogaster marker strain y w (grey, two wildtype copies of bam) is shown for reference. There is no statistical difference in bam expression of the bam hypomorph with and without Wolbachia (P = 0.253; t-test).