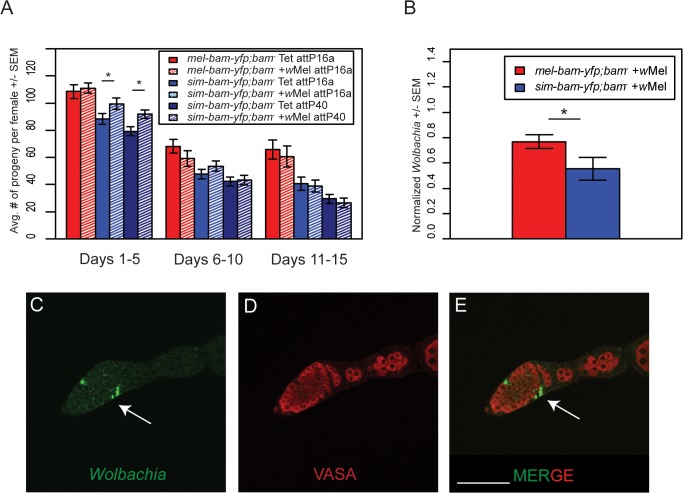
Fig 9. Wolbachia interacts with sim-bam-yfp; bam −in females.
(A) Female fertility assay. One female and two tester males were allowed to mate and the trio was transferred to a new vial every five days. Fertility is shown as the average number of progeny per female +/- SEM for each vial. (t-test, *P<0.05). All comparisons between mel-bam-yfp; bam −+wMel and mel-bam-yfp; bam −Tet are not significant. All day 6–10 and 11–15 comparisons between sim-bam-yfp; bam −+wMel and sim-bam-yfp; bam −Tet are not significant. N ranged between 38 and 40 females at start of experiment; due to female mortality N ranged between 26 and 33 at end of experiment. (B) q-PCR for wMel titer was performed from ovarian DNA from the indicated genotypes using Wolbachia-specific primers. (t-test, *P<0.05). N = 3. (C-E) Wolbachia localizes to the SSCN in sim-bam-yfp; bam −flies. Ovaries from sim-bam-yfp; bam −flies were stained with antibodies to Vasa (red) and Hsp-60 (green), which recognizes Wolbachia. Wolbachia preferentially accumulate at the somatic stem cell niche (arrow) of the germarium. Scale bar, 50μm.