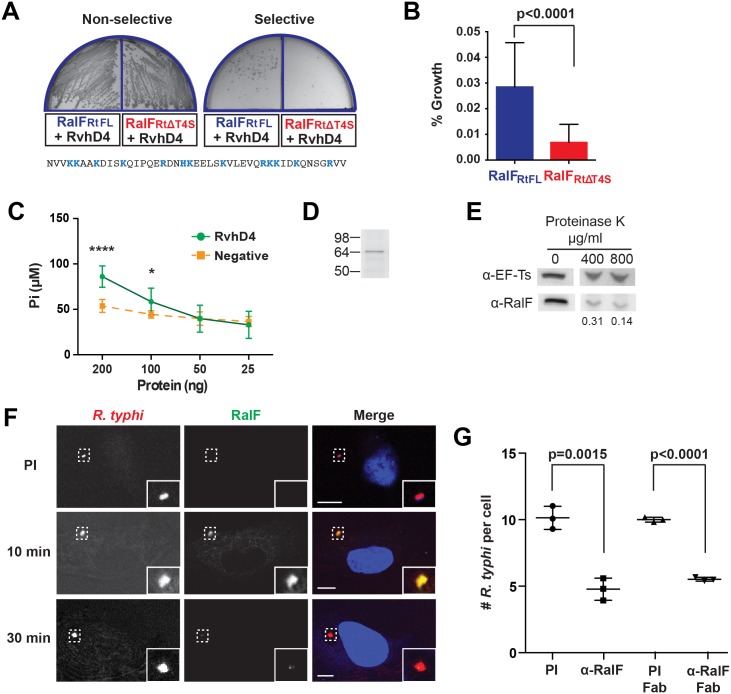
Fig 1. R. typhi RalFRt interacts with RvhD4 and is expressed early during host cell invasion.
(A) Bacterial two-hybrid (B2H) assay reveals an interaction between RalFRt and RvhD4. ralF RtFL and ralF RtΔT4S were cloned into pTRG (prey) and rvhD4 was cloned into pBT (bait) of the B2H system. Constructed bait and prey plasmids were co-transformed into BacterioMatch II reporter electro-competent cells. Transformants were screened on non-selective plate (left) and positive interactions were identified on dual selective screening plate (right). The amino acid sequence deleted from ralF RtΔT4S (positively charged residues are colored blue) is shown at bottom. (B) Quantification of bacterial growth in the B2H assay described in panel A. Percent growth of CFUs of reporter cells harboring recombinant plasmids on dual selective screening medium was calculated relative to CFUs obtained on non-selective medium. Error bars represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments (Student’s two-sided t-test). (C) R. typhi RvhD4 exhibits ATPase activity. A series dilution of purified RvhD4 in assay buffer was incubated with reagent for 30 min at 21°C. The inorganic phosphate (Pi) released from ATP was quantified by measuring absorbance at OD 620 nm. As a negative control, a non-related R. typhi protein (RT0600) was assayed. Error bars represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * p = 0.01, **** p<0.0001; Student’s two-sided t-test. (D) Protein immunoblot of recombinant RvhD4 (~64 kDa) used in ATPase activity assays described in panel C. (E) RalFRt is surface exposed. Purified R. typhi was treated with 400 μg/mL or 800 μg/mL Proteinase K or in buffer alone for 1 hr. Lysates were resolved and immunoblotted for RalF or the R. typhi cytoplasmic control protein, elongation factor Ts (EF-Ts). Densitometry was performed using ImageJ and the intensity of RalF was normalized to EF-Ts. Representative image from two independent experiments is shown. Intensity of RalF normalized to EF-Ts and relative to untreated control is shown below the immunoblots. (F) RalF is expressed during early infection. HeLa cells infected with R. typhi for 10 and 30 min were fixed and R. typhi and RalF detected with rat anti-R. typhi (red) and affinity purified rabbit anti-RalFRt (green) antibodies, respectively. DAPI (blue) is shown in the merged image. Boxed regions are enlarged to show detail. Pre-immune (PI) cells were treated with rabbit PI serum in place of anti-RalFRt antibody. (Scale bar: 10 μm). (G) Anti-RalFRt IgG and Fab fragments inhibit R. typhi host cell infection. HeLa cells were infected with partially purified R. typhi pre-absorbed for 30 min with 20μg PI IgG serum, anti-RalFRt IgG, PI Fab fragments or anti-RalFRt Fab fragments. Cells were fixed 2 hrs post infection and R. typhi and the cell membrane detected with anti-R. typhi serum and Alexa Fluor 594 wheat germ agglutinin, respectively. The number of R. typhi per host cell was counted for 100 individual host cells in three independent experiments and normalized to PI serum. Error bars represent mean ± SD (Student’s two-sided t-test).