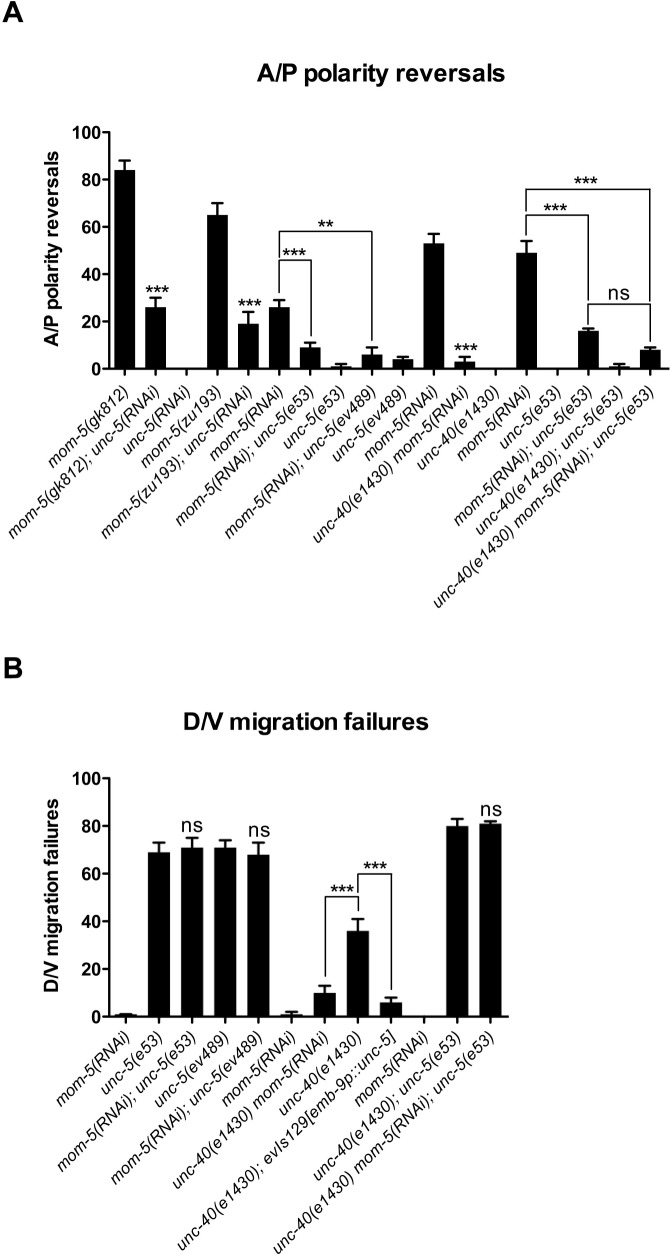
Fig 3. mom-5 mutant phase 3 A/P polarity reversals are rescued by impairing unc-5 or unc-40 function or both, while impairing mom-5 can rescue unc-40 D/V defects in a manner that is strictly dependent on unc-5 function.
(A) Percent posterior DTC phase 3 A/P polarity reversals in mom-5(gk812) or mom-5(zu193) alleles treated or not with unc-5(RNAi) plus unc-5 and unc-40 single and unc-40; unc-5 double mutants treated or not with mom-5(RNAi). (B) Percent posterior DTC phase 2 D/V migration failures in unc-5 and unc-40 single and unc-40; unc-5 double mutants treated or not with mom-5(RNAi). Also shown are the effects of evIs129[emb-9p::unc-5] on DTC phase 2 migration failures of unc-40(e1430). The corresponding raw data including the data for the anterior DTC are presented in S3 Table. Error bars indicate the standard error of the sample proportion. Comparisons of A/P polarity reversals were made between mom-5 mutant animals treated or not with unc-5(RNAi), or between mom-5(RNAi) of N2 compared to mom-5(RNAi) of Netrin receptor mutants. Comparisons of D/V defects were made between Netrin receptor mutants treated or not with mom-5(RNAi) and unc-40(e1430) in the absence or presence of evIs129. ***P <0.00001; **P<0.001; ns = not significant (P≥0.01). The corresponding control for RNAi was grown on empty vector RNAi feeding bacteria.