Figure 1. Targeting Hh signaling at the level of the GLI transcription factors.
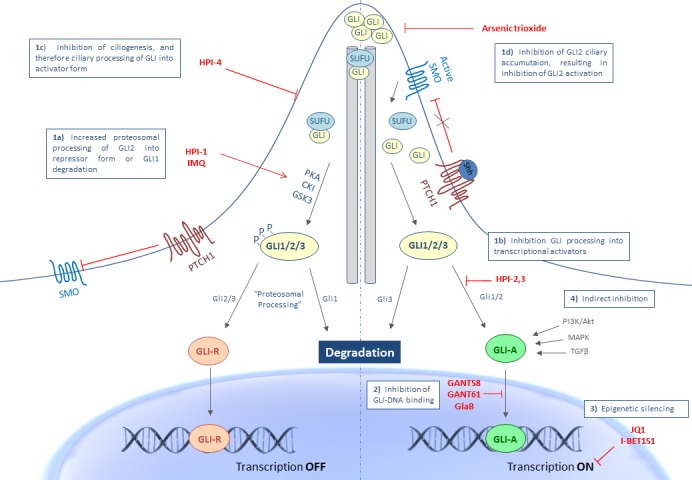
GLI inhibition can occur at different levels in the activation process of GLI transcriptional output: 1a. Increased proteosomal processing of GLI2 into repressor form or GLI1 degradation with HPI-1 or IMQ. 1b. Inhibition of GLI processing into its activator form by HPI-2/3, 1c. Inhibition of ciliogenesis and therefore processing into the activator form with HPI-4, 1d. Inhibition of GLI2 ciliary accumulation and thus activation of of GLI2 by ATO. 2. Inhibition at the level of GLI-DNA binding through GANT58, GANT61 or GlaB, 3. Through epigenetic silencing with JQ1 or I-BET151 and 4. Through indirect inhibition of non-canonical signaling pathways known to activate the GLI transcription factors. Abbreviations: CKI, casein kinase 1; GANT, Gli-ANTagonist; GlaB, Glabrescione; GLI, Glioma-associated oncogene homologue; GLI-A, activator form of GLI; GLI-R, repressor form of GLI; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; HPI, Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor; IMQ, imiquimod; P, phosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; PTCH1, patched 1; SHH, sonic hedgehog; SMO, smoothened; SUFU, suppressor of fused.
