Figure 2. Inhibition of cell growth and induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by AIB1 knockdown in gastric cancer cells.
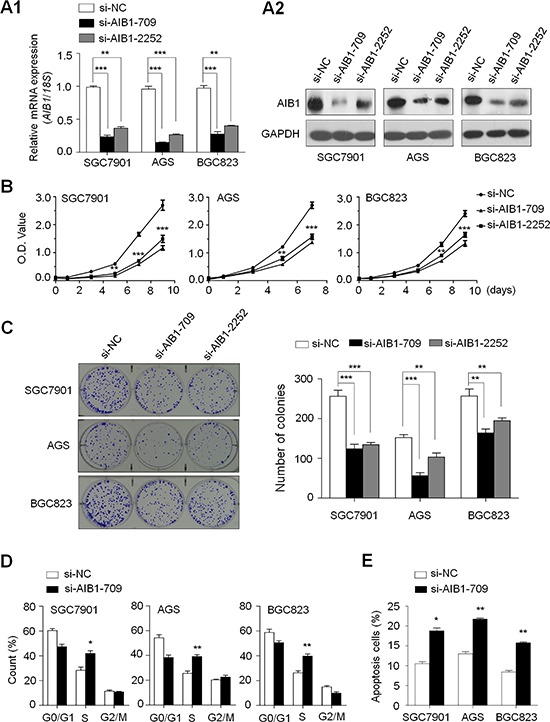
Knockdown of AIB1 mRNA A1. and protein A2. by using two different siRNAs (si-AIB1-709 and si-AIB1-2252) in gastric cancer cell lines SGC7901, AGS and BGC823 was evidenced by qRT-PCR and western blot, respectively. 18S rRNA was used as a normalized control for qRT-PCR assay. GAPDH was used as loading control in western blot analysis. ***P < 0.001. B. AIB1 down-regulation significantly inhibited cell proliferation in gastric cancer cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. C. The effect of AIB1 knockdown on cell growth was further confirmed by colony formation assay. Left panel shows the representative images of colony formation in cells transfected with si-AIB1s or si-NC. Quantitative analysis of colony numbers is shown in right panel. Data were presented as mean ± SE of values from three different assays. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. D. Cells were transiently transfected with si-AIB1-709 or si-NC. DNA content was measured by flow cytometry to determine cell cycle fractions. The fraction of cells in each cell cycle phase was indicated in the figures. Data were presented as mean ± SE of values from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. E. Cells transiently transfected with si-AIB1-709 or si-NC. Apoptotic cells including early and late apoptotic cells were measured 72 hours after transfection by flow cytometry analysis of Annexin V-FITC/PI double-labelled cells. The experiment was repeated three times and data were presented as mean ± SE. **P < 0.01.
