Figure 6. Modulation of major signaling pathways by AIB1.
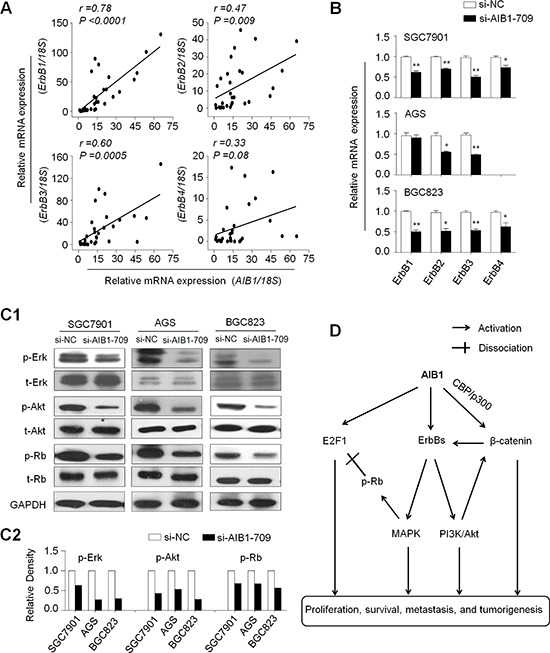
A. qRT-PCR assay was used to evaluate the mRNA expression of AIB1 and ErbB receptors in primary gastric cancers (n = 30). Linear regression analysis was performed to assess the correlations between them. 18S rRNA was used as a normalized control. B. qRT-PCR assay was performed to test the effect of AIB1 knockdown on the expression of ErbB receptors in gastric cancer cells. 18S rRNA was also used as a normalized control. *P < 0.05;**P < 0.01. C1. Cells transfected with si-AIB1-709 or si-NC were lysed and lysates were subjected to western blot assays. The antibodies against phospho-Erk (p-Erk), total Erk (t-Erk), phospho-Akt (p-Akt) and total Akt (t-Akt) were used to determine the effect of AIB1 down-regulation on the activities of the MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. The antibodies against Rb and phosphorylated Rb (p-Rb) were used to test the effect of AIB1 down-regulation on Rb signaling. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C2. Shown was quantitative illustration of levels of p-Erk, p-Akt, and p-Rb using densitometry to measure the density of the corresponding bands on Western blot shown in (C1). D. Schematic model of molecular mechanisms underlying oncogenic role of AIB1 in gastric cancer. AIB1 overexpression or amplification can up-regulate the expression of ErbB receptors and subsequently activates ErbB-mediated signalling pathways such as MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. AIB1 also modulates Rb/E2F1 signaling through promoting phosphorylation of Rb and co-activating E2F1 transcriptional activity. In addition, the previous evidences and the findings in the present study demonstrate that AIB1 can activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling through different mechanisms. Taken together, AIB1 overexpression or amplification promotes gastric cancer cell growth and invasiveness through modulating major signaling pathways, ultimately contributing to poor prognosis of gastric cancer patients.
