Figure 3.
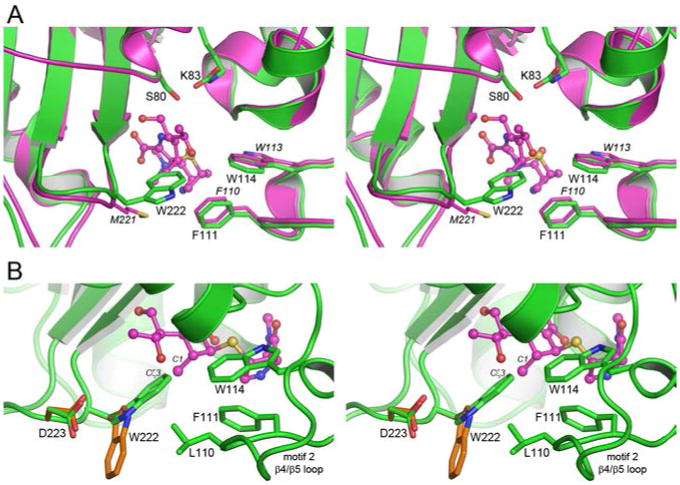
The Trp222 side chain in OXA-51 would occlude the active site. (A) Stereoview of the active site of OXA-51 (green) superimposed on OXA-23 (magenta). The location of meropenem in the OXA-23 structure is shown as magenta ball-and-stick. The position of Ser80 in OXA-51 shows the location of the site of acylation. (B) Stereoview of the outer end of the OXA-51 active site, showing the location of Trp222 and the residues from the β4/β5 (Leu110, Phe111 and Trp114) loop which make hydrophobic contacts with Trp222. Meropenem from OXA-23 is shown as magenta ball-and-stick. The critical clash between the indole ring of Trp222 and the C1 methyl atom of the substrates is indicated. The alternate rotamer configuration of Trp222 from energy minimization calculations is shown as orange sticks, and the small rotation of the Asp223 side chain is also indicated.
