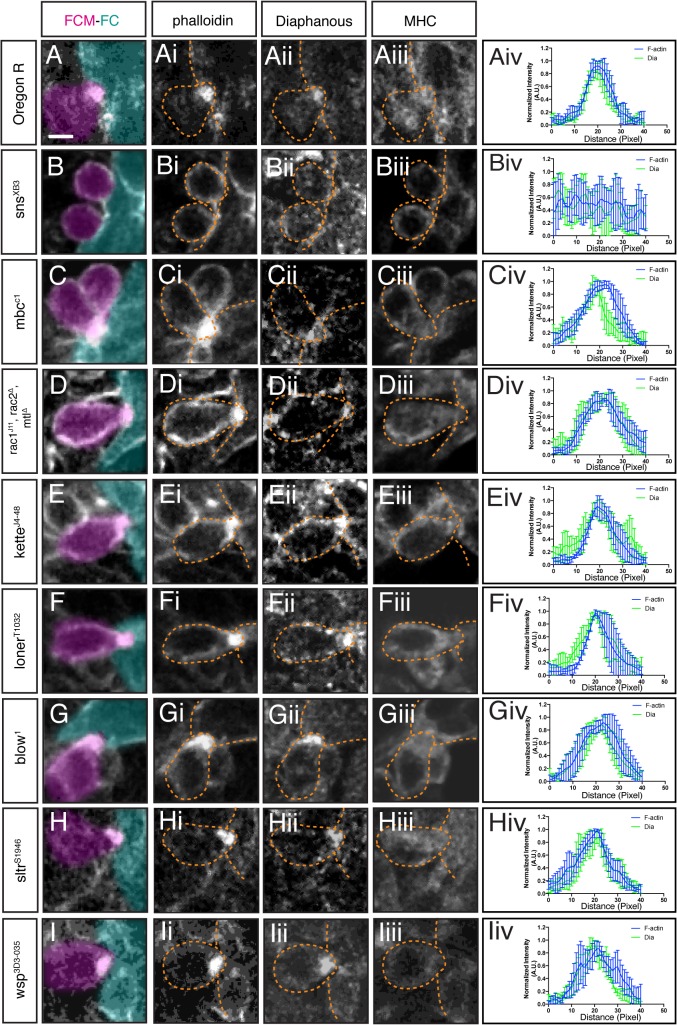
Fig 2. Dia localization at the fusion site is dependent on FC/FCM recognition and adhesion, but independent of regulators of Arp2/3.
Stage 15 embryos stained with phalloidin (i.), antibodies against Dia (ii.), and Myosin Heavy Chain (iii., MHC). Phalloidin labels F-actin (focus and sheath) at the fusion site; MHC identifies myoblasts. FCM (magenta) and FC/Myotube (turquoise). A-iv. Dia localization in FCM and FC/myotube in a wild-type embryo during myoblast fusion. Dia accumulates at the fusion site. The averaged fluorescence intensity curve (Aiv, n = 5) in wild-type embryos confirms Dia colocalization with actin. B-iv. In sns mutants, no F-actin focus is formed and no specific accumulation of actin or Dia are observed. Average fluorescence intensity curve of sns mutant embryos (Biv, n = 5) supports that Dia does not accumulate at the fusion site and is cytoplasmic. C-E-iv. In rac, mbc, and kette mutants, SCAR activity is lost, an enlarged focus is observed at the fusion site, and Dia is enriched at the fusion site. Fluorescence intensity curves confirm Dia and actin colocalization in rac (Civ), mbc (Div), and kette (Eiv) mutants (n = 5/genotype). F-iv. In loner mutant embryos, Dia accumulates at the F-actin focus, as confirmed by the fluorescence intensity curves (n = 5). G-I-iv. In blow, sltr(Dwip) and wsp mutants, where WASp-mediated actin remodeling is lost, Dia accumulation at the fusion site is unaffected. Fluorescence intensity curves confirm the colocalization of Dia and F-actin in blow (Giv), sltr(Dwip) (Hiv), and wsp (Iiv) mutants (n = 5/genotype). Scale bar: 2.5μM.