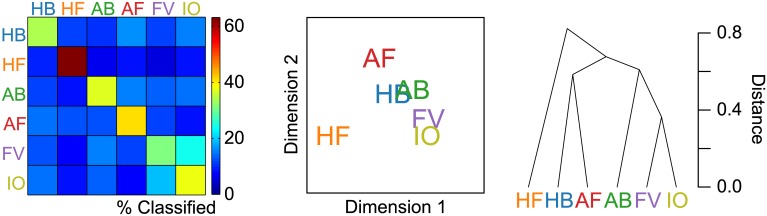
Fig 3. Category-level classification results.
All electrodes and time samples of the brain response were used together in the six-class category-level classification. An equal number of observations from each category were used. Left: Confusion matrix showing proportions of classifier output. Rows represent actual labels and columns represent predicted labels. Values along the diagonal indicate proportions of correct classifications. Mean accuracy for this classification was 40.68%, compared to chance-level accuracy of 16.67% (Fig 2). Middle: Multidimensional scaling (MDS) plot derived from the confusion matrix, visualizing the non-hierarchical structure of the representational space. MDS dimensions are sorted in descending order of variance explained. Right: Dendrogram visualizing the hierarchical structure of the representation. The Human Face category is most separate from the other categories, while the two Inanimate categories form the tightest category cluster.