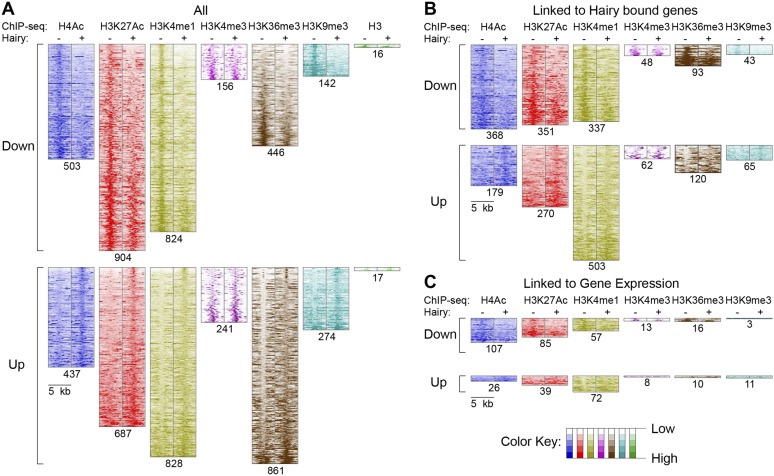
Figure 4. Pervasive genome-wide chromatin effects of Hairy.
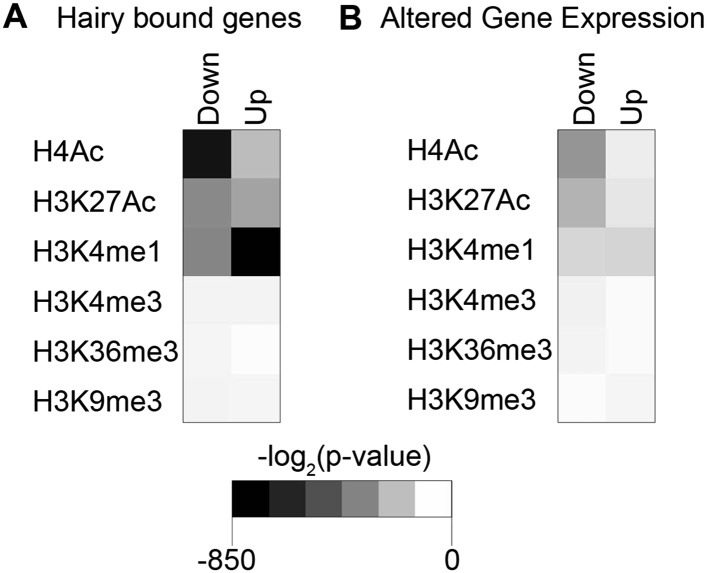
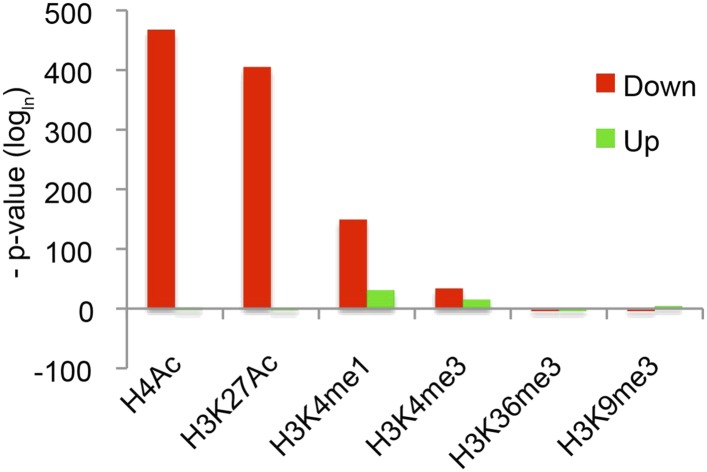
(A) All reduced (top) and increased (bottom) chromatin marks in the genome for H4Ac, H3K27Ac, H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K36me3, H3K9me3 and H3 shown as heatmaps for 5 kb windows from the center of significantly affected regions before (−) and after (+) Hairy induction. The number of affected regions indicated below each mark. (B) Affected chromatin regions associated with Hairy-bound genes show preferential enrichments for H4Ac, H3K27Ac, and H3K4me1. All affected regions were assigned to closest genes, and those in the vicinity of Hairy-bound genes are shown. (C) Subset of modified regions from (B) that were linked to genes transcriptionally regulated by Hairy. Significance of enrichment for chromatin modifications shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1A,B.