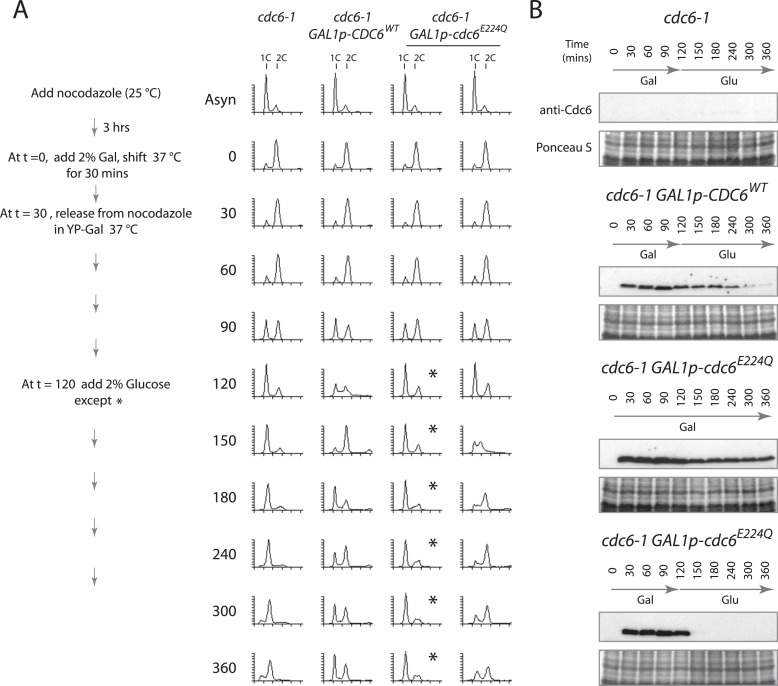
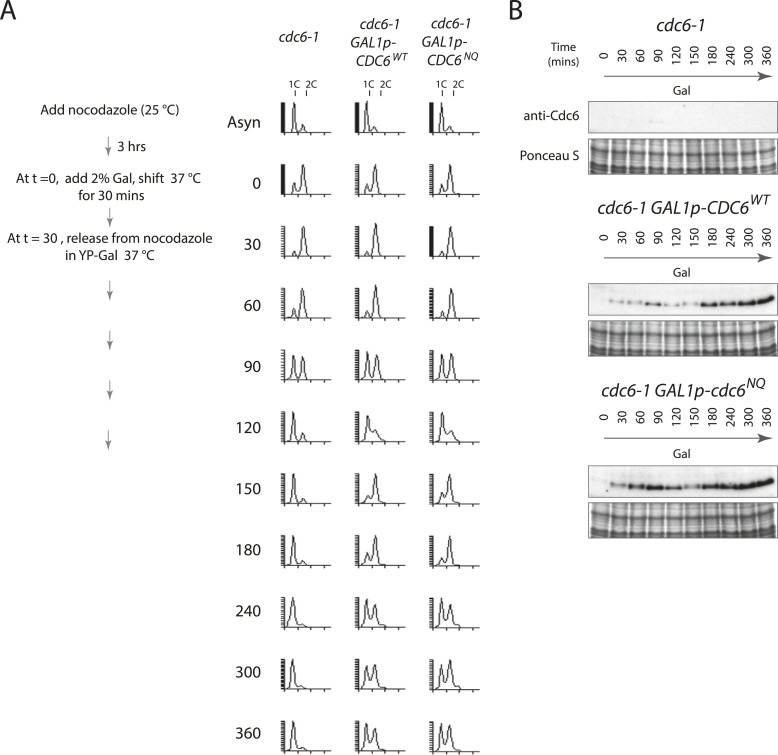
Figure 4. Cdc6 removal after MCM loading bypasses ATPase requirement and is sufficient to allow DNA replication.
(A) Synchronization protocol (left) and flow cytometry profiles (right) of yeast strains M378 (cdc6-1), M4455 (cdc6-1 GAL1p-CDC6::LEU2), and M4531 (cdc6-1 GAL1p-cdc6-E224Q::LEU2). Asynchronous cells were arrested in G2/M for 3 hr with nocodazole, shifted up to 37°C for 30 min (from t = 0 to 30 min), and then released into G1-phase at 37°C expressing no additional Cdc6, GAL1p-CDC6 or GAL1p-cdc6-E224Q. GAL1 promoter-driven CDC6 expression was shut off at t = 120 min by the addition of glucose except where marked by an asterisk. Identical flow profiles to M4531 were seen using an independent cdc6-1 GAL1p-cdc6-E224Q integrant strain, M4530. (B) Cdc6 Western blots (top panels) and total protein (bottom panels) by Ponceau S staining of the samples are shown in panel A. The addition of glucose at 120 min causes Cdc6 wild-type protein to disappear and this occurs more rapidly for the Cdc6-E224Q mutant.