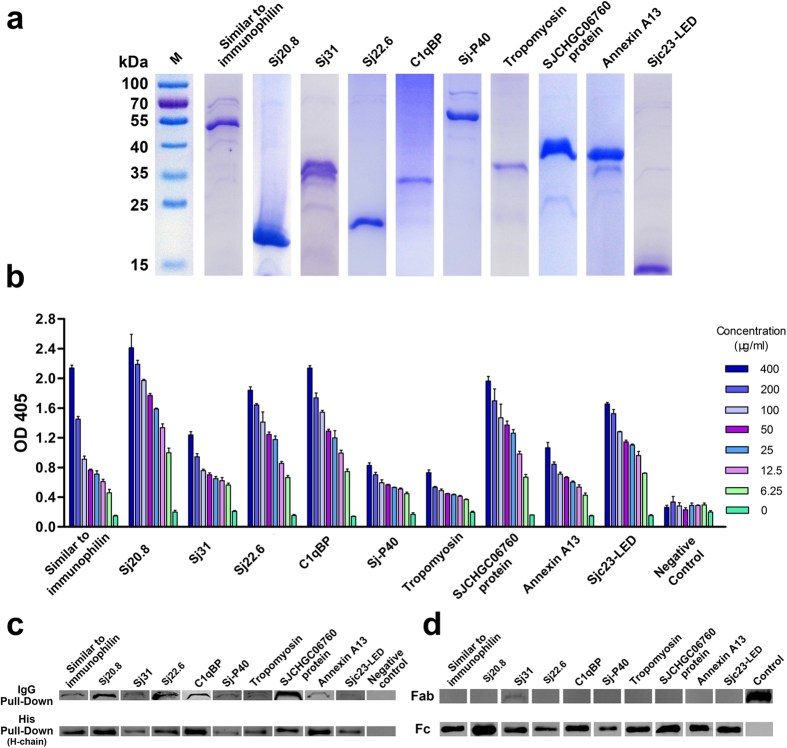
Figure 5. Binding characterization of the ten schistosomal proteins with non-immune human immunoglobulin G.
(a) SDS-PAGE confirmation of ten His-tagged recombinant proteins. (b) Binding of the ten proteins with human non-immune IgG using an ELISA assay. Purified human plasma IgG from individuals without schistosomiasis was applied to ELISA plates and used to evaluate the affinity of ten proteins for it. All ten proteins showed capacity for binding to human IgG. (c) Binding of the ten proteins with human non-immune IgG in the pull-down assay. Human IgG-Sepharose and His-tagged proteins immobilized on Ni-NTA agarose resin were used as bait to capture the fusion protein or human IgG, respectively. The affinity was detected by Western blot using the appropriate antibodies. The binding capacity of the ten proteins to human IgG was confirmed using both the IgG pull-down and His pull-down assays. (d) The binding of human IgG domains to the ten proteins in the pull-down assay. The Fab and Fc fragments of human IgG were incubated with fusion protein-conjugated particle. After washing, the binding was detected by Western blot. Sjc23-LED was used as a positive control for binding with the Fc fragment and a negative control for binding with the Fab fragment. An unrelated His-tagged protein was used as a negative control for the Fc fragment, and the purified Fab fragment was used as a positive loading control for detection. All ten proteins bound to the Fc fragment, while only Sj31 marginally precipitated the Fab fragment with a dim band.