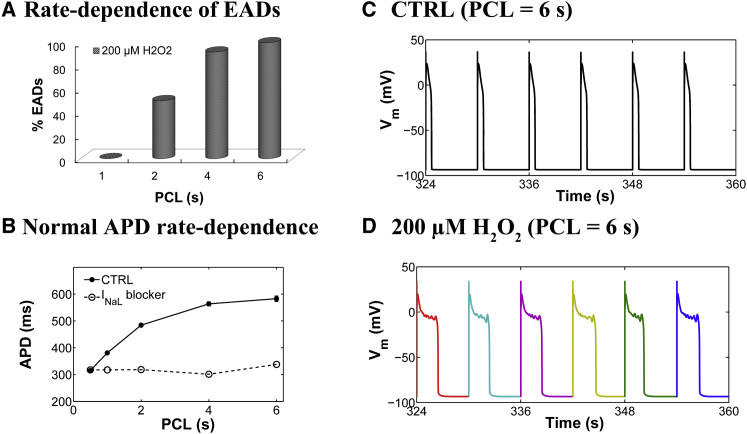
Figure 2.
(A) Simulated rate dependence of H2O2-induced EADs. The EAD incidence rate is predicted to be higher at low pacing rates (long PCLs) in the presence of 200 μM H2O2. (B) PCL dependence of APD under control (CTRL) conditions (solid circles) and in the absence of baseline INaL (open circles). Under control conditions, the APD increases with PCL and this rate-dependent increase is abolished in the absence of INaL. (C) Simulated APs from a 6 s PCL protocol in the absence of oxidative stress (CTRL, 0 μM H2O2) (12,500 Ca2+ release units). Results for the last six consecutive APs are shown. (D) Simulated APs, all of which exhibit EADs, under conditions of elevated oxidative stress (200 μM H2O2). To see this figure in color, go online.