Fig. 3.
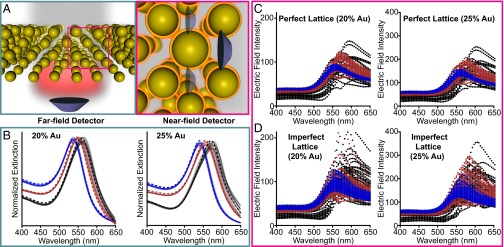
Far- and near-field plasmonic properties of high volume fraction superlattices. (A) Scheme depicting far-field (Left) and near-field (Right) plasmonic properties. (B) Far-field extinction spectra (solid traces) for 10 randomly generated superlattices incorporating nanoparticle polydispersity (10%) and variation in lattice location (5%); the dashed lines are for the “perfect” superlattices that do not include inhomogeneity. The simulations incorporate the experimental particle sizes determined in Fig. 3 for ∼10-nm (blue), ∼20-nm (red), and ∼40-nm (black)-diameter spheres. Each trace represents a single superlattice simulation. (C) Distribution of the near field at the surface of each particle in a perfect lattice (Left, 20% Au; Right, 25% Au). (D) Distribution of the near field at the surface of each particle in an imperfect lattice (Left, 20% Au; Right, 25% Au). The structural parameters describing each structure are listed in Table 2; each film has an ∼500-nm edge length and is in an index of 1.33.
