Fig. S2.
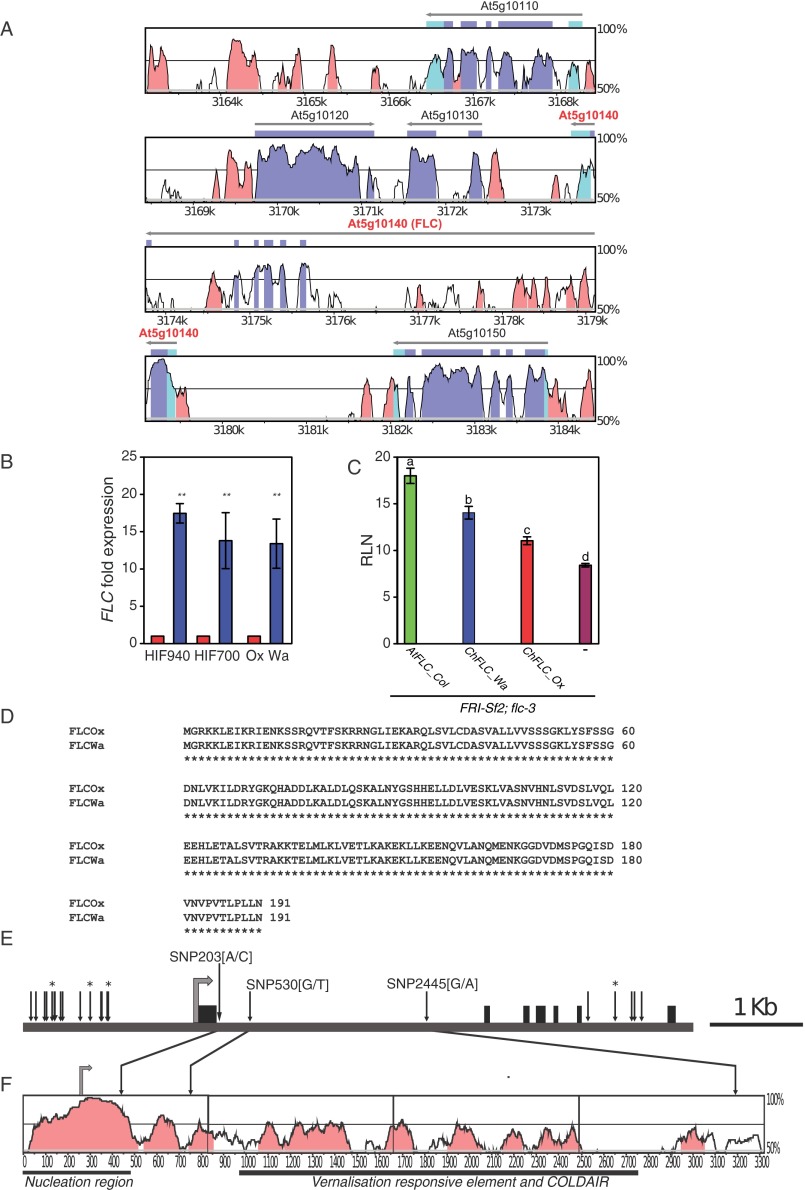
QTL-LG6 Validation and cloning of ChFLC. (A) Vista plot (genome.lbl.gov/vista/index.shtml) showing DNA sequence conservation of the C. hirsuta QTL interval within the A. thaliana genome around the FLC gene. The 19,801-bp C. hirsuta sequence that was aligned spanned 21,308-bp of the A. thaliana genome. Conserved sequences are indicated by color as follows: noncoding sequence (pink), 5′ and 3′ UTRs (light blue), and the coding sequence (purple). (B) ChFLC expression in segregating HIF940 and HIF700 and parental strains showing five visible rosette leaves is significantly higher in genotypes carrying the ChFLCWa allele (blue) compared with genotypes with the ChFLCOx allele (red). **P < 0.01 (Student’s t test). (C) Rosette leaf numbers (RLN) of transgenic A. thaliana FRISf2; flc-3 lines complemented with AtFLCCol0, ChFLCWa, and ChFLCOx alleles and untransformed controls (−) show that the ChFLCWa allele is stronger compared with ChFLCOx. Letters indicate significant differences between groups as indicated by ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey’s test (P < 0.01). Bar charts in B and C show the mean values and SDs. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of ChFLCOx- and ChFLCWa-encoded proteins revealed no amino acid changes between alleles. (E) Diagram of the ChFLC locus. Black boxes indicate exons, and the gray arrow shows the translation start codon. Vertical arrows indicate the positions of polymorphisms between the Ox and the Wa allele. Arrows marked with * indicate InDels and those without SNPs (see Table S2 for further details). The position, relative to the adenine in the start codon, and nucleotide change are given of the three SNPs within the first intron. (F) Vista plot showing DNA sequence conservation between A. thaliana and C. hirsuta FLC genes, including 245 nt of the promoter, the first exon, and the first intron. The gray arrow indicates the FLC start codon, and the following functional regions of A. thaliana FLC intron 1 are underlined: nucleation region (27, 28), vernalisation responsive element (VRE; ref. 30), and COLDAIR long ncRNA (the transcription start site of COLDAIR is within the VRE region; ref. 29). Vertical arrows indicate the position of three SNPs that differentiate the Ox from the Wa allele in the ∼3-Kb fragment that is sufficient to recapitulate functional differences between the two ChFLC alleles. Note how SNP [A/C] at position 203 is located within a region of high-sequence homology with the nucleation region in A. thaliana where FLC silencing is initiated by the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PHD-PRC2) during cold exposure.