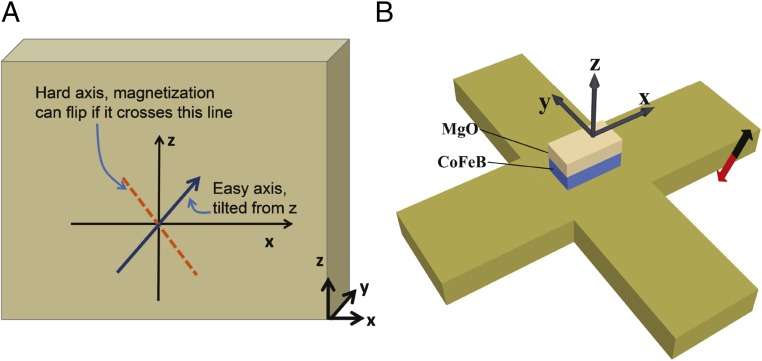
Fig. 1.
Schematic description of switching mechanism and device structure. (A) Orientation of the easy axis and hard axis of an otherwise perpendicularly polarized magnet with slightly tilted anisotropy. (B) The fabricated device structure. The underneath Hall bar is composed of Ta and is used to generate spin accumulation through spin–orbit interaction and also to detect the direction of magnetization through anomalous Hall effect measurement. Current flowing along the short direction of the magnet (along the y axis) leads to a deterministic switching.