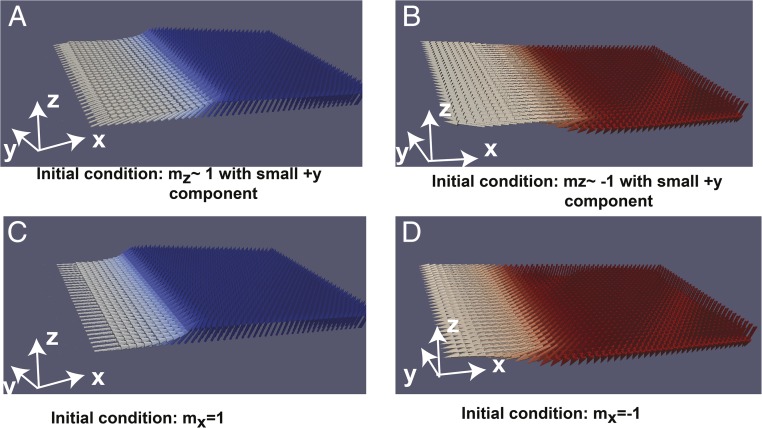
Fig. 5.
Micromagnetic simulation. (A) Starting from the magnet saturated in +z state with a small +y component, the system is allowed to relax. The final equilibrium state of the magnet is such that the moments in the wedge region point toward +x. Thus, average magnetization tilts toward +x. (B) Similarly starting from the magnet saturated in −z state, the magnetization tilts toward −x at equilibrium. (C) Starting from the magnet in +x, caused by spin accumulation in +x direction due to −y directed current pulse, the magnet evolves to +z state due to the tilt in the anisotropy axis. (D) Starting from the magnet in −x, caused by spin accumulation in −x direction due to +y directed current pulse, the magnet evolves to −z state. The blue arrow indicates that the magnetic moment is in +z, whereas the red arrow indicates it is in −z state.