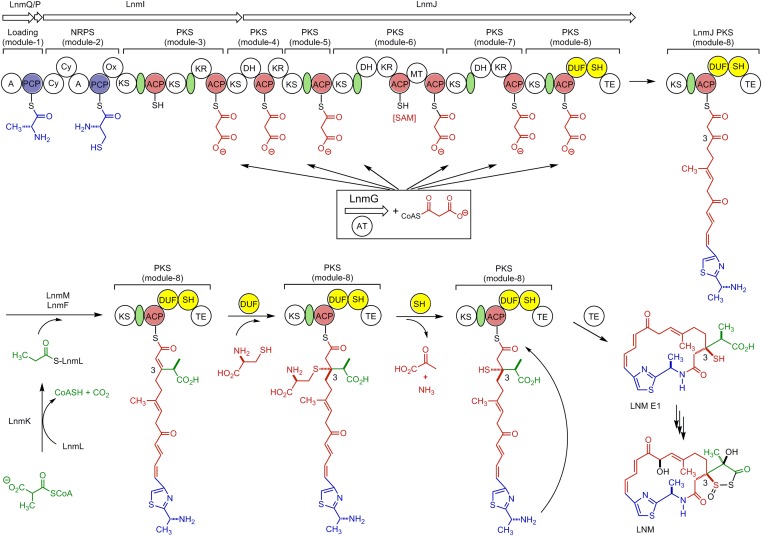
Fig. 1.
Proposed biosynthetic pathway for LNM featuring (i) the LnmQPIJ hybrid NRPS-AT–less type I PKS with the discrete LnmG AT loading the malonyl CoA extender units to all six PKS modules (21, 23, 24), (ii) the LnmKLMF enzymes catalyzing introduction of the β-alkyl branch at C-3 (25-27), (iii) the DUF and SH domains of PKS module-8 of LnmJ catalyzing sulfur incorporation into C-3 of LNM from l-cysteine characterized in this study, and (iv) LNM E1 as the nascent product of the LNM hybrid NRPS-AT-lee type I PKS (28), setting the stage to investigate the tailoring steps that convert LNM E1 to LNM. Color coding indicates the moieties installed by NRPS (blue), PKS (red), β-alkyl branch (green), and other tailing enzyme (black), and the green ovals denote AT docking domains. A, adenylation domain; AT, acyltransferase; Cy, condensation/cyclization; DH, dehydratase; DUF, domain of unknown function; KR, ketoreductase; KS, ketosynthase; MT, methyltransferase; Ox, oxidation; PCP, peptidyl carrier protein; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SH, PLP-dependent cysteine lyase domain; TE, thioesterase.