Fig. S4.
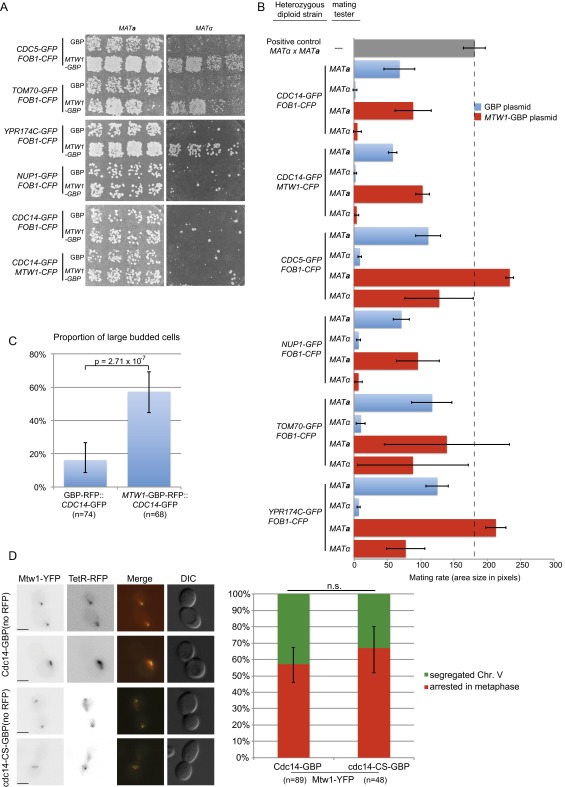
Kinetochore SPIs can produce a CIN. A selection of SPIs were recreated in diploid cells (heterozygous for the GFP tag). These diploids, which contain either the GBP or MTW1-GBP plasmids, were patched onto plates and mated with either MATa or MATα strains. (A) We found that the MTW1-GBP plasmid causes three GFP strains to have elevated chromosome loss (TOM70, YPR174C, and CDC5). In contrast, we found no increased chromosome loss for the Mtw1-Cdc14 SPI. (B) These data are quantified and shown relative to both positive and negative controls; the error bars are SD of the mean. (C) The Mtw1-Cdc14 SPI causes cells to arrest as large budded cells; error bars are 95% binomial confidence intervals and P value is a Fisher’s exact test. (D) Examples of large budded cells of a strain encoding a marked chromosome V locus (ura3-1::3xURA3-tetOx112 TETR-RFP) with MTW1-YFP and either CDC14-GBP or cdc14-CS-GBP are shown both with separated chromosomes or unsegregated chromosomes. Note that the GBP alleles in this case are not RFP-tagged and that GBP binds to YFP equivalently to GFP. The proportion of large-budded cells, arrested specifically in metaphase with unsegregated chromosomes, is quantified and does not differ for Cdc14-Mtw1 compared with the CDC14 mutant-Mtw1. Error bars are 95% binomial confidence intervals. n.s., not statistically significant. (Scale bars, 5 µm.)